Discharge is normal for any healthy woman and is observed throughout life. They are usually divided into physiological and pathological (leucorrhoea). Their type and quantity are influenced by many factors. The main one is hormonal status. The number of white clots in women’s discharge depends on it. Color, smell and consistency may change depending on the processes occurring in the body.
If you have stress incontinence, you leak small amounts of urine unintentionally, especially when you cough, sneeze or laugh, or when you exercise or lift heavy objects. Urinary incontinence can occur at any time during pregnancy, but is most common in the last trimester.
Muscles pelvic floor are under additional stress during pregnancy and are also subject to hormonal changes. Therefore, any increase in abdominal pressure caused by coughing, sneezing, laughing, or other activities that push these muscles can cause small amounts of urine to leak.
Normal
Normal vaginal discharge looks like thin, cloudy mucus due to epithelial impurities. This is noticeable in the gasket - a yellowish mark remains on it. Discharge is formed as a result of the activity of the vaginal glands. They are present in smaller quantities in other reproductive organs. If you have discharge in the form of white lumps that resemble cottage cheese, you can think about vaginal candidiasis, or thrush.
Urinary incontinence can be difficult and distressing; however, you should mention the problem to your doctor, who will be able to advise you on Kegel exercises, which should help reduce the problem if you practice them regularly. It's also important to empty your bladder when you need to. You may want to wear a sanitary pad for extra reassurance.
During pregnancy, you are more susceptible to urinary tract infections. Most often, such infections are limited to the bladder, when they are known as cystitis. Symptoms of cystitis include frequent, urgent need to urinate and painful sensation burning sensation when passing urine, there may be some blood in the urine. Sometimes the infection can move from the bladder to the kidneys. In this case, you may also have pain in the lower back on one side, heat and may cause nausea or vomiting.
A woman’s discharge, if she is healthy, does not cause burning, irritation of the mucous membranes or itching of the skin. This is due to anatomical and physiological features: the vaginal mucosa and lactic acid bacteria, which are its permanent inhabitants, produce mucus and lactic acid, which perform protective functions. A constant slightly acidic pH environment is created< 4,5. Поддержание такого уровня pH не даёт возможности развиваться патогенным микроорганизмам. Также происходит процесс самоочищения: слизь выводит отмерший эпителий, лейкоциты, остатки менструальной крови, секрет бартолиновых желёз. Объём выделений не превосходит 1 чайной ложки.
Sometimes a urinary tract infection is present but does not cause any symptoms. Prompt treatment of urinary tract infections is especially important during pregnancy because if the infection reaches the kidneys, it can cause early labor. Urinary tract infections are caused by bacteria that enter the body through the urethra and multiply. Such infections are likely to be more common during pregnancy because the influence of hormones on the urinary tract slows the passage of urine.
If you have any symptoms of a urinary tract infection, contact your doctor immediately. The doctor will take a midstream urine sample, and the sample will be sent to a laboratory to determine the type of bacteria causing the infection. Your doctor can prescribe a seven to 10-day course of antibiotics that is safe for you and your baby. Symptoms usually improve within a few days of starting treatment. Because some urinary tract infections are asymptomatic, all pregnant women have their urine tested at their prenatal visits, and if bacteria is found, appropriate antibiotics are prescribed.
Any changes in color, quantity, smell, etc. are regarded as a pathology.
You need to know that the discharge includes microflora (5 - 12 types of microorganisms): bacteria, fungi, viruses, which are constantly present in the vagina in small quantities. The cervix, its cavity, tubes and ovaries are normally sterile and do not contain any microorganisms. Normal vaginal microflora consists of:
Are there different types of preeclampsia?
This is one of the most serious conditions associated with pregnancy as it can quickly become life-threatening for both mother and baby if not treated as early as possible. Preeclampsia was previously known as toxicosis of pregnancy because it is believed to be caused by a toxin present in the bloodstream of a pregnant woman. It can be classified as follows: depending on the etiology and symptoms.
Causes of pathological discharge
Although the exact causes are not yet known, certain placental abnormalities have been found to be responsible for causing the complication. Once the egg implants itself on the wall of the uterus, it produces several root growths that attach it to the lining. Blood vessels in the uterus supply nutrients to the villi so they can grow and develop into the placenta. These blood vessels also change shape to help the placenta grow properly. Sometimes blood vessels fail to transform correctly, interrupting the flow nutrients into the developing placenta.
- lactic acid bacteria (10 7);
- streptococci, fungi, bacteria, enterococci;
- conditionally - pathogenic microorganisms.
The latter include fungi of the genus Candida, gardnerella, and mycoplasma in very small (10 4) quantities.
The mere fact of identifying these microorganisms is not evidence of disease.
The “normality” of discharge is determined by the woman herself, since the normal amount and consistency can vary. In some patients, scanty or heavy discharge in women is normal, if their amount does not change throughout life in the absence of pathology.
At the same time, abnormal kidney function causes essential proteins to leak into the mother's urine from the bloodstream, causing symptoms of proteinuria. The exact factors that prevent the proper transformation of blood vessels in the uterus are unknown.
Complete prevention is not possible due to unknown etiology. For this reason, it is very important to have regular prenatal checkups and follow your doctor's instructions for a healthy pregnancy. Although, precautions taken to prevent high blood pressure during pregnancy do not always minimize the chances of developing preeclampsia, taking the following measure may help reduce the risk. Expert advice is recommended before considering such preventive measures.
Normal menstrual cycle
The type and amount of vaginal secretion directly depends on the flow menstrual cycle: before menstruation there is a sharp increase in their number. This is due to age, and, therefore, to hormonal levels. Girls have odorless discharge and no itching. When hormonal levels stabilize, the amount and volume of discharge decreases significantly. They become more watery, their volume increases significantly, the color changes to pale yellow upon the onset of sexual activity: the contents of the partner’s urethra are added.
What are the signs and symptoms of preeclampsia?
But since you will not be able to detect these symptoms, you must keep an eye out. Although symptoms such as swollen arms and legs and weight gain are normal during pregnancy, be sure to call your doctor if you experience sudden changes in weight or swelling.
What are the possible complications of preeclampsia?
Future cardiovascular disorders and heart failure.
- Premature labor and delivery Lung problems.
- Damage to the liver and kidneys.
- Stroke.

After unprotected sex, the discharge becomes like white flakes, and its volume also increases sharply. After a few hours, everything returns to the original norm: the secretion dilutes, its quantity decreases.
After protected sex, vaginal discharge becomes white and resembles a thick lubricant.
Preeclampsia Differential diagnosis
Positive results in either or both of the above tests require additional diagnostic procedures, including. Your doctor may also order tests and exams to evaluate the health of the fetus.
Treatment and management of preeclampsia
- Chronic hypertension without preeclampsia.
- Primary seizure disorders.
- Chronic renal failure.
Treatment of mild preeclampsia
Women with mild preeclampsia are placed on bed rest until delayed and are closely monitored in hospital for any signs of worsening. A urine test to detect certain proteins in the urine that may indicate liver damage.
Treatment of severe preeclampsia
- Blood analysis.
- Measurement blood pressure at least 4 times a day.
- Monitoring fluid intake.
Normal during pregnancy
One of the signs of pregnancy is a delay in menstruation and discharge. white. In the first trimester, as a result of hormonal changes, the secretion changes: it becomes liquid, whitish or transparent, stretchy. There are no unpleasant sensations.
Modifications occur in the third semester of pregnancy: about a week before birth, secretion increases sharply. Immediately before childbirth, white lumps appear, and when the cervix dilates, a clot of mucus leaves it - this is the opening of the cervix and the beginning of the labor process.
Incidence, prevalence and mortality of preeclampsia
The C section may be performed if it is too early to induce labor. Cystitis, also known as cystitis, occurs predominantly in women. However, men are not protected from this vulgarity. On average, every second woman suffers from cystitis at least once in her life. Men are better protected by having a longer urethra than women, so they rarely get the disease. Often home remedies and medicinal herbs are sufficient to clear up a bladder infection, but in other cases antibiotics must be used.
During lactation, the nature of the vaginal contents changes again: it becomes thick and unproductive.
During menopause, upon examination, a “dry vagina” is observed due to scanty discharge. This is due to low estrogen levels and changes in the mucous membrane of the uterine wall, which thins and atrophies.
This is why a doctor should always be consulted when a burning sensation is heard and released. In the case of a bacterial urinary tract infection, symptoms vary in severity. Often, serious urination is associated with the burning of the first signs of cystitis. It is then important to act immediately to prevent the bacteria from spreading further and ascending to the kidneys. It is important to keep the belly warm and to ensure proper hygiene. Cystitis is also infectious. Therefore, changing towels daily and cleaning the toilet daily should be obvious.
Causes of pathological discharge
White discharge, or leucorrhoea, is a manifestation of an infection or other pathological process. Currently, more than 100 factors have been identified that affect the color, consistency, smell, amount of leucorrhoea and cause pain, burning, itching or other unpleasant sensations.
The main reasons for the appearance of pathological leucorrhoea include:
If a bladder infection is not treated, it can develop into a chronic condition that occurs again and again at regular intervals of weeks or months. Cystitis often occurs when bacteria enters the urethra from the intestines. Because the female urethra is much shorter than the male's and also closer to the anus, it becomes infected very quickly. However, other bacteria or fungi can also cause cystitis. However, cystitis can have completely different causes. Cold and wet clothing, going to a swimming pool or sitting on cold objects can have a positive effect on the development of this urinary tract disease.
- inflammatory diseases of the female genital area or urological;
- allergic reactions;
- helminthiases;

- neoplasms (cysts, polyps, tumors);
- foreign bodies in the uterus;
- thinning of the uterine wall after 40 years (atrophic processes) associated with hormonal disorders;
- hyperglycemia.
Pathological discharge may be a sign of insufficient personal hygiene, sudden climate change; prolapse of the vaginal walls.
Symptoms of cystitis can occur together, but also occur alone. There is often a slight pain in the abdomen, which is especially noticeable when external pressure is applied to the bladder. In addition, there is a constant desire to urinate, but urine is often released only in drops. In addition, severe burning during watering is a typical symptom of cystitis. In most cases, the urine becomes darker and has bad smell. This can lead to blood as well as abdominal cramps.
We do not treat bladder infections; bacteria can grow and the kidneys become infected. Then there are symptoms such as chills and severe pain in the lower back where the kidneys lie. A safe diagnosis can only be made by a doctor. In addition to the general overview and examination, a urine sample provides information. The so-called middle purinine bundle is considered for various substances. On the one hand, white blood cells appear when they are present, and on the other hand, the urine contains nitrite in true cystitis.
According to the origin of the pathological process, leucorrhoea is the result:
- colpitis;
- inflammatory processes in the cervix;

- pathologies in the uterus;
- changes in fallopian tubes Oh.
From the cervix
Normally, cervical secretion is insignificant. In pathological conditions, the amount of discharge can increase sharply. The most common cause of colpitis is chlamydia or gonorrhea - sexually transmitted infections (STIs). White discharge with this pathology can change into purulent discharge with traces of blood.
It is a metabolic product that is not found in urine in healthy urinary tracts. If cystitis is not a simple inflammation, then additional tests may be carried out. This includes, for example, ultrasound, in which case the kidneys are usually also examined. White flocculants in urine are proteins that the body often secretes in blisters and kidney infections in large pieces called flocs.
Mild and straightforward cystitis can be treated with home remedies in many cases. It is important to keep your stomach and legs warm at all times. Bottle with hot water, placed on the back or stomach may help relieve symptoms. In order for the germs present in the bladder to be flushed out, fluid must be added to the body. For this purpose, at least two to three liters should be drunk throughout the day. Herbal teas or bear leaf tea, which has an antibacterial effect, are very suitable.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is much more common than gonorrhea: according to statistics, 6 - 8% of the world's population suffers from this infection. With this disease, the leucorrhoea, as the infection progresses, gradually acquires a greenish tint and flows down the vaginal wall. The process is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen and lower back.

Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea causes a slight, creamy, yellowish-white leucorrhoea that changes color over time. It occurs acutely, accompanied by high fever, pain in the lumbar region, along the inner thighs, and lower abdomen. The infection quickly spreads to all organs of the reproductive system. IN short time can lead to “sticking” of the fallopian tubes due to the accumulation of inflammatory fluid and cause infertility.
Trichomoniasis
STIs that cause the formation of pathological discharge in women include trichomoniasis. Since it is transmitted sexually, it is classified as a sexually transmitted disease. Characterized by profuse, watery, foamy leucorrhoea with unpleasant smell. They are accompanied by itching, burning, and pain. If the process invades the urethra, urination is also disrupted and pain occurs.

Bacterial vaginosis
The reason for the formation of abundant whitish-gray leucorrhoea of a homogeneous consistency with a specific smell of rotting fish is bacterial vaginosis. Itching and burning may be absent or moderate, pain is not bothersome, urination is not impaired, and there are no lumps in the discharge. It is caused by conditionally pathogenic bacteria - Gardnerella vaginalis, together with polymicrobial associations of other anaerobes. With reduced immunity, the number of lactobacilli decreases, while active reproduction of conditionally pathogenic microflora occurs, which includes gardnerella, which leads to vaginal dysbiosis. Usually, upon examination, there are no signs of inflammation - this is an important sign for diagnosis. But the foul smell of fish is clearly noticeable. It intensifies when exposed to alkali (soap, shower gels, semen, etc. are alkaline). Isonitrile gives it a characteristic odor that cannot be confused with anything else. It is a product of the breakdown of amines that appear as a result of the activity of anaerobic conditionally pathogenic bacteria.
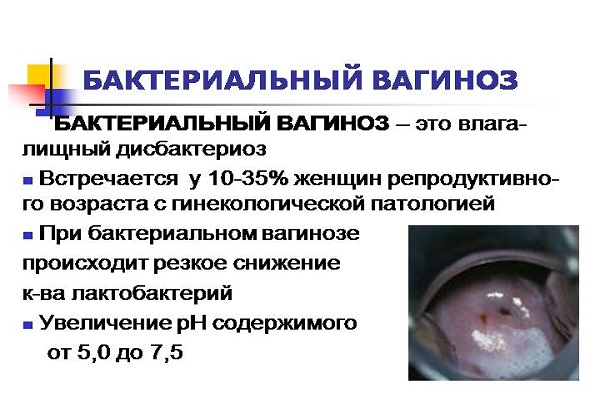
If dysbiosis caused by Gardnerella is not treated in time, nonspecific vaginitis develops. It is differentiated from candidiasis, which causes a picture of vaginitis. Causes various menstrual cycle disorders.
Candidiasis
Thrush is accompanied by discharge with white clots. Most often, with candidiasis (a fungal infection caused by fungi of the genus Candida), white discharge in lumps is observed. There are several strains of the microorganism. The fungus is normally found in a woman’s body - it is a conditionally pathogenic microflora. Under certain conditions, the amount of the fungus increases, or a more pathogenic strain is added, i.e., it is not the Candida fungus itself that plays a role in the development of pathology, but a sharp increase in its amount.

Clinically, thrush is manifested by copious cheesy discharge with an unpleasant sour odor. The discharge is characterized by white flakes, accompanied by severe itching, pain, burning in the vaginal area, and redness. The itching intensifies significantly in the evening, prevents sleep and can last all night. The process of urination is accompanied severe pain, which do not subside for a long time. This is observed when the pathological process moves to the urethra. A constant burning sensation is caused by abundant irritating mucous membranes. curdled discharge in the form of flakes.
In the chronic form of candidiasis, itching and burning may be minor or completely absent. In this course of the disease, pathological leucorrhoea comes to the fore.
A gynecological examination reveals the presence of white plaque and films on the labia majora and minora and the clitoris with a specific smell of bread or sour milk. When the plaque is removed, an eroded surface and bleeding are revealed. The appearance of curdled masses in thrush is present regardless of the background of hormones or the phase of the menstrual cycle. Without treatment, candidiasis affects large areas.

Causes of mycotic lesions:
- decreased immunity due to severe chronic diseases ( diabetes, HIV);
- antibiotic therapy;
- hormonal imbalances;
- contraception;
- douching;
- improper diet;
- obesity;
- tendency to constipation.
Diabetes mellitus is a favorable background for Candida, since high sugar content promotes increased proliferation of yeast and the spread of the process, providing a breeding ground for them.
There are also everyday factors that are an impetus for faster proliferation of fungi. These include: wearing synthetic underwear, excessive consumption of coffee and strong tea, spicy seasonings and baked goods, use of soap and rough gels for intimate hygiene, frequent change of sexual partners, colds and existing chronic diseases that contribute to a decrease in immunity.
Pathological secretion from the cervix is produced during erosion and dysplasia. Then, as the process progresses, they become purulent and streaks of blood appear.
Other pathology
Uterine discharge is a sign of an inflammatory disease or neoplasm - tumors, polyps. Initially they are transparent, watery and odorless. Over time, they become purulent with a brownish tint.
Occurs rarely: with inflammation or cancerous tumors. They are yellowish, watery mucus that accumulates in the pipes.
There are also pathological conditions in which white discharge, with or without clots, is not associated with an infectious lesion. These include:
- dermatitis of the external genitalia;
- cervical polyps;
- foreign objects in the vagina (tampons);
- malignant neoplasms of the female reproductive system.
It is very important to pay close attention to your health and monitor any changes in your vaginal discharge. The appearance of leucorrhoea with lumps, flakes, a pungent odor and other pathological signs is a signal to visit a gynecologist. The faster this happens, the greater the chances of avoiding serious illnesses and their complications. By contacting a doctor early, it is possible to prevent inflammation before symptoms appear.
A serious attitude towards health will never ignore the issue of discharge with white flakes in women.
Regularly before and after menstruation, a healthy woman experiences clear or slightly cloudy vaginal discharge. She doesn't give them any attention special attention, because, being the norm, they do not create discomfort, do not have an unpleasant odor, and do not cause itching and burning in the perineum. Thanks to the discharge, the vagina is cleansed of dead epithelial cells, remnants of menstrual blood, and mucus. Sticky white discharge during ovulation is also normal.
But suddenly, instead of the usual ones, white vaginal discharge appears, reminiscent of kefir. The woman immediately tries to get to the bottom of the reason for their appearance.
Causes of white discharge in women
- Candidal vaginitis (candidiasis), popularly called thrush, is one of the most common causes of white, cheesy discharge. The abundance of discharge is not the only complaint of women, because when it appears, swelling and redness of the external genital organs, burning, itching, white coating on the clitoris, between the labia minora and majora. Leucorrhoea has a sour smell. In addition, foamy white discharge after sexual intercourse, accompanied by pain, confirms the presence of thrush. Many people know about its signs and, without delay, begin treatment on their own, while forgetting that their partner also needs to be treated, because the fungal pathogen is sexually transmitted, although candidiasis is not a sexually transmitted disease. Its treatment must be approached with all seriousness. If independent treatment does not give the desired result, you need to contact a gynecologist to clarify the nature of the cheesy discharge.
- Uncontrolled use of antibiotics without antifungal drugs disrupts the vaginal microflora, promoting the rapid proliferation of fungi, which causes thrush.
- Oral contraceptives, influencing a woman’s hormonal levels, provoke the appearance of leucorrhoea. A gynecologist will help you choose a contraceptive or change it.
- Pregnancy is a huge hormonal change in the female body. The amount of progesterone increases, immunity decreases, which sharply increases the activity of fungi. An inflammatory process begins in the genitals, accompanied by cheesy discharge, itching and burning.
- Mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis and other sexually transmitted diseases have symptoms similar to those of thrush. They can cause foamy and cheesy discharge with an unpleasant odor of spoiled fish or rotten hay. If there is even the slightest doubt about the safety of sexual intercourse, you should immediately contact a specialist. Identifying these diseases in the early stages makes it possible to get rid of dangerous bacteria. An advanced version of the disease can lead to infertility.
- Endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, thyroid pathology) are also the cause of the appearance of discharge characteristic of candidiasis.
Having dealt with some of the causes of discharge with white flakes in women, I would like to emphasize that a gynecologist must diagnose the disease in order to begin qualified treatment in a timely manner.

