The second name of which is cyanocobalamin, which can accumulate in the human body. It is found in the kidneys, liver, lungs and spleen. Unlike other vitamins, cyanocobalamin is water soluble.
What is vitamin B12 for? Its main task is to promote the production of new blood cells. Its other functions are limited to participation in regulating the production of amino acids and nucleic acids.
Observed effects of vitamin deficiency include: megaloblastic anemia, methylmalonic acid, neurological disorders. The supply of this vitamin from supplemented diets of nursing mothers was more than twice that of mothers who ate traditional foods. This study also found that higher levels of this vitamin in vegetarian milk influenced occasional consumption of meat products and fish rather than dairy products. Products enriched with this vitamin. Dr. Roman Pawlakmg Małgorzata Desmond.
He completed his doctorate at the University of Southern Mississippi. At his university he teaches: “Nutrition and Wellness, Nutrition in Metabolism and Physiology, Nutrition and Nutrition.” Dr. Pawlak is a Fellow of the American Society of Nutrition, the American Dietetic Association, and a member of the American Dietetic Association Evidence Review Committee on Vegetarian Diets. Professor Pawlak's particular interest is dietary prevention based on the activities of churches and social institutions.
In addition, vitamin B12 contains such a rare and valuable microelement for humans as cobalt. Other vitamins do not contain it. The body cannot produce B12 on its own. Therefore, it is very important to eat foods that contain it. This vitamin is found in animal products.
The role of B12 is great for the growth of a child’s body.
Roman Pawlak is the author of I Am the Lord Who Heals You and co-author of A Vegetarian Mother and Her Child. Małgorzata Desmond graduated with a degree in Nutritional Medicine from the University of West London and a Master's Degree in Dietetics from the University of Warsaw medical university and a course in Nutritional Epidemiology at Imperial College London. Until recently Director of Nutrition at a private university in the UK and Ireland. He is currently a staff member at the pediatric clinic of the Monument Institute for Children's Health Center in Miedzlesi, where he conducts research on the effects of a vegetarian diet on children's health.
Beneficial features
Few people can correctly answer the question of what vitamin B12 is for. What does it help with? Let's look for answers.
Cyanocobalamin helps the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow, so that the level of hemoglobin in the blood remains at the desired level. B12 prevents cells from experiencing oxygen starvation. This vitamin also maintains normal blood pressure.
Read more about this in the article by Dr. Similar to how other vitamins in this group dissolve in water. Unhealthy ailments - inflammation of the mouth, bad smell body, painful menstrual complaints. In some cases there may be allergic reaction or anaphylactic shock, that is, the body’s reaction resulting from a disproportion between the desired and actual intake of the vitamin. Animal products - liver, heart, kidney, lean meat, fish, shellfish, cheese, eggs.
We use gymnastics classes to improve muscle mass and strength. Most young and old people who visit training rooms know that muscles are not only about the aesthetics of a man's silhouette, but also about health until later in life. Working muscles that produce hormones called myokines generally protect us from many diseases, including: cancer. Muscles are also a major consumer of sugar; Therefore, when their mass remains quite high level, we are not at risk of diabetes.
Recent studies have shown that sufficient vitamin B12 in cells promotes increased bone growth. This is the main reason that cyanocobalamin should be in children's diets as the child grows.
The synthesis of proteins and amino acids thanks to B12 helps build muscles.
Cyanocobalamin plays an important role in ensuring the vital activity of cells spinal cord. Consequently, it also affects the muscles controlled by the nervous system. What conclusion follows from this? Without B12V human body muscles will not grow. This substance also regulates energy exchange in the human body.
The health benefits of exercise can be multiplied, but the topic is a completely separate article. On this moment However, we must mention that lifting enthusiasts are looking for products to support their work on large and strong muscles.
For example, according to the Lexicon of Modern Therapeutics, adenosine cobalamin “has anabolic and analgesic effects, increases appetite, and causes weight gain.” It's no secret that muscles, like other tissues, must grow vitamins, as well as other nutrients. We can also use the example of vitamin A, whose super-active analogues have been linked to skin problems and cancer.

B12 increases the production of protein compounds, that is, it has an anabolic effect. The protein obtained in this way accumulates in the human body.
Its effect on the nervous system comes down to the fact that cyanocobalamin regulates our emotions and also develops. What do you need to know about vitamin B12? Surprisingly, it can relieve insomnia, which arose as a result of a restructuring of sleep patterns.
Likewise, some vitamins, taken in therapeutic doses far beyond basic requirements, exhibit anabolic activity such as muscle atrophy or stimulation of weight gain. This was a post-operative course in which the patient's body was in a catabolic phase, and the catabolic effect of cortisol was further exacerbated. Here again, the administration of this vitamin resulted in a 6-month increase in body weight in more than 33% of the patients participating in the study. But the processes of muscle regeneration and hypertrophy are not only protein anabolism, but also myogenesis, i.e. production of new cell nuclei and muscle fibers.
If the amount of cyanocobalamin in the body is sufficient, then the person will not experience depression. He is also not at risk of dementia, confusion, and his memory will be excellent.
B12 improves lipid metabolism, and also maintains cholesterol at the desired level and prevents the development of liver steatosis.
Cyanocobalamin is indispensable for human immunity. If there is a deficiency of it in AIDS, then the disease develops more intensively.
Myogenesis is carried out by accompanying muscle fibers, stem cells called satellite cells. For example, Mikhailov demonstrated that vitamin B12 and B9, administered together, have a pronounced activating effect on the regeneration of muscles and nerve shafts after mechanical damage to motor neurons.
A very similar experiment was carried out by Polish scientists in similar fields. The researchers divided the pigs into two groups here, injecting a large dose of local anesthetic with two groups that simulated muscle damage due to its depopulation. Unlike control animals, pigs from the experimental group also received BU injections in all animals after the administration of anesthetics. Muscle necrosis was observed, however, administration of vitamin B12 accelerated the regeneration of damaged skeletal muscle by facilitating phagocytosis of dead cells and stimulating myogenic satellite cell proliferation.
Effect of cyanocobalamin
Let's look at why vitamin B12 is needed in the body. It is known to have the following effects:
- takes part in the synthesis of fats and proteins;
- reduces fatigue;
- increases endurance;
- improves brain activity;
- participates in hematopoiesis;
- increases immunity;
- regulates nervous activity;
- restores mucous membranes.

Vitamin B12 simply catalyzes reactions associated with the synthesis of nitrogenous bases that form nucleic acids. Therefore, its level is especially important for rapidly dividing cells such as red blood cells, immune cells and satellite cells. At this stage, it should be remembered that muscle fiber fibroblasts are the basis of muscle hypertrophy in response to mechanical overload. This phenomenon is even called “myocyte dominance.” The fact is that the nucleus initiates and controls the critical process of protein synthesis, which leads to the rate of generation of cellular proteins from the number of nuclei.
Useful properties for hair
The main points why vitamin B12 is needed have been discussed. However, it is no less needed for hair. It not only enhances the growth of strands, but also has a whole range of useful functions, such as:
- Serves as a material for the construction of new healthy curls. If there is insufficient supply, the hairs will be thin and weak, and their growth will stop.
- Helps increase their volume.
- Reduces the amount of hair we lose daily by strengthening the hair roots.
- It has regenerating properties, thanks to which it restores damaged hair well. The strands are no longer brittle, and the ends no longer split.
- Hair growth is enhanced and stabilized.
- Stimulates blood circulation, allowing nutrients to reach the roots better. Due to this, the hair becomes thick, acquires shine and beauty, and becomes healthier.
When there is a lack of cyanocobalamin in the body, the scalp is the first to suffer - the roots are weakened. Because of this, the hair can no longer be held in place and falls out en masse. They do not grow or recover.
Therefore, muscle fibers, due to their vital functions to support high protein anabolism, are multinucleated, unlike most cells in our body. And when mechanical overload training forces them to intensify anabolic processes, replenish damaged ones and create additional, contracting protein forces, they acquire additional nuclei, absorbing reproductive satellites under these conditions. Thus, it has long been established that an increase in skeletal muscle mass certainly depends on mitotic activity, that is, on the rate of division of satellite cells.
What role does vitamin play in bodybuilding?
People looking to improve their performance probably know what vitamin B12 is for. If you are involved in bodybuilding, then remember that cyanocobalamin causes fats to participate in metabolism. Thanks to this, the body's energy supply improves during strength training.
B12 regulates the functions of platelets, due to which they are able to quickly deliver oxygen and nutrients to the muscles.
Anabolic steroids are generally extremely useful therapeutic agents due to their ability to stimulate protein synthesis, muscle regeneration, bone calcium, and red blood cell production and growth. This is why they are theoretically used to treat various muscle deficiencies, osteoporosis, anemia and shortness of breath. In practice, their use has serious limitations.
Because androgens or male sex hormones can promote virilization in women and precocious puberty in large doses. Thus, we know, for example, that promising effects of such cognitive therapy have been obtained in the form of increased protein anabolism and in the treatment of underweight and short-lived children with pituitary gland diseases. And these results may have indicated an increase in strength, because the stronger and stronger muscles, the less they trembled when they held the same weight position for a long time.
This vitamin also helps stimulate the nervous system muscle work, due to this, coordination of movements improves.
Symptoms of B12 deficiency
In order to determine the deficiency of such a useful substance in the body, it is enough to do a blood test. If hemoglobin is low, then most likely this vitamin is also lacking. The consequence of low levels of cyanocobalamin is B12-deficiency anemia, in which red blood cells cannot carry oxygen normally, as well as slowly progressive dysfunction nervous system.
Fortunately, cyanocobalamin deficiency is easily treated, but the problem lies in its early detection. Magnetic resonance imaging studies suggest that the resulting cerebral atrophy in children can be reversed with rapid addition. On the other hand, if the defect is too late to be detected, then treatment will not lead to a complete cognitive and physiological turnaround. Often accompanied by hyperactivity and lack of concentration. These symptoms overlap with autistic disorders.
In addition, in both cases, obsessive-compulsive behavior is observed in some children, disorders of speech, writing and reading comprehension, inhibition and grooming. Unfortunately, very few of them will do the proper research, which can lead to misdiagnosis and a “diagnosis” of autism. Young children and infants suffering from cyanocobalamin deficiency often report gastrointestinal problems that may be confused by generalized colic or gastritis. A small one who speaks little, is apathetic, and not very mobile, can be considered simply polite and calm.

You can find out about a lack of B12 in the body if you have the following symptoms:
- Nervous system disorders. The person becomes irritable, easily excitable, has frequent depression, blurred vision, poor reflexes, and hallucinations.
- Digestive disorders: lack of appetite, food is not digested, the liver is enlarged, frequent constipation.
- Constant lethargy, fatigue, dizziness, drowsiness, frequent headaches, tinnitus, difficulty breathing.
Vitamin complexes
It is very important to periodically monitor the content of this useful substance in the body. If its deficiency is detected, you must urgently purchase a complex with it in any form at the pharmacy.
Infants are much more vulnerable than adults because their central nervous system develops dynamically. Vitamin B12 deficiency in adults develops relatively slowly - from several months to several years. Healthy mothers have a cobalan reservoir of 25 mcg. This completely covers their metabolic needs.
Accordingly, quick additional treatment, individually selected, has an invaluable effect on the baby’s health. Correct, early diagnosis and action taken can lead to rapid improvement. Unfortunately, some areas of the brain may remain permanently damaged. The extent to which levels of proper functioning are restored depends on the age at which therapy is started, the extent of the deficit, and how long it has been “latent.”
Known sources of vitamin B12:
- Ampoules of the drug "Cyanocobalamin". They should be injected intramuscularly every day. The package will be enough for a course of ten days.
- Vitamin complex in tablets, for example, Neurovitan or Neurobion. Take it one pill after meals once or twice a day for 10 days.
Unfortunately, for some nutritional and mineral components, this does not apply to the severe deficiencies described here. Meanwhile, folic acid masks the signs of anemia and macrocytosis, which are the first symptoms of cobalamin deficiency. It is surprising, but surprising, that women prior to conception, during pregnancy and lactation are not regularly studied for such deficiencies.
Ladies thinking about expanding their family should proactively undergo a morphological examination. Improvement in blood parameters occurs after a dozen or so days of treatment. B vitamins are often thrown in the same bag as those that support the nervous system. Part of the truth is that supplementing with B vitamins increases mental clarity and has a positive effect on brain function, but one vitamin in particular stands out in this pool.
You should not consume more vitamin than required according to the instructions. It is best if you balance your diet and ensure that you have enough of this substance in your diet. Can also be taken additionally vitamin complex, but it's worth choosing one. In case of an excess of cyanocobalamin and the occurrence of hypervitaminosis, the following symptoms may appear:
- nervous excitement;
- heartache;
- rash;
- pulmonary edema;
- blockage of blood vessels;
- arrhythmia.
Foods containing vitamin b12
What foods contain cyanocobalamin? It must be remembered that this vitamin is found mainly in animal products. Very small amounts of it are found in plant foods, such as:
- spinach;
- hop;
- vegetable leaves;
- salad greens;
- yeast;
- sea kale.
As a rule, a person consumes these products in small quantities. While to get the required B12 norm you would have to eat a lot of them.
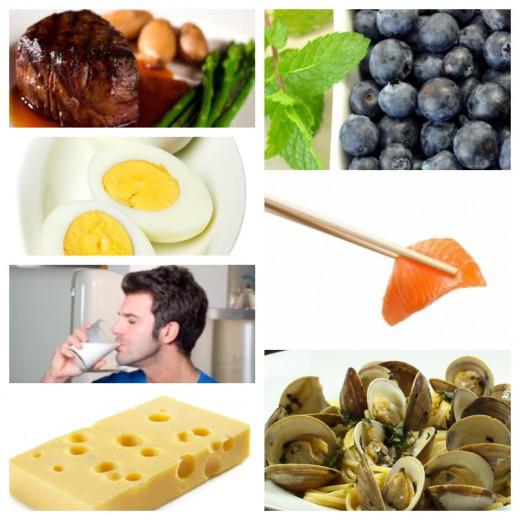

Cyanocobalamin is not produced in the body, so it must be taken in the form of food. Most of it is in:
- liver, kidneys;
- yolks;
- dry skim milk;
- in many types of fish (such as sardines, salmon, herring);
- as well as in oysters and crabs.
A little less of it in:
- chicken and meat (such as beef or pork);
- seafood;
- hard cheeses;
- as well as in fermented milk products.
Some B12 is found in regular milk and homemade soft cheese.
In the most dangerous position are strict vegetarians who do not eat not only meat and eggs, but also dairy products.
Some people who prefer food plant origin, do not see anything dangerous in this. They argue that many poor people in the East eat mostly grains and vegetables, but these people do not suffer from B12 deficiency or the diseases that usually accompany B12 deficiency. The explanation for this phenomenon lies in the fact that small insects still live in unprocessed grains, which serve as a source of cyanocobalamin.
Daily requirement
So, what vitamin B12 is needed for is clear, but how much do you need to consume this substance for the body to work smoothly? As it turned out, quite a bit - 0.000003 g per day and 0.001 g per year. However, if we cannot provide this meager amount, we will become seriously ill.
Women who are about to give birth, as well as those who are in the lactation period, should consume it twice as much. Elderly people and those who adhere to a strict vegetarian diet, smoke or drink significant amount alcohol, must purchase B12 and take it additionally.
Conclusion
Now you know what vitamin B12 is needed for and what it is eaten with. As practice shows, thanks to the amazing properties of such a small but so active substance, a person is able to avoid depression, protect his body from digestive problems, and be significantly enriched with vital energy. The main thing is to take moderation when consuming vitamins.
Vitamin B12 is a cobalt-containing vitamin with very important functions. Therefore, it is very important to know why the body needs vitamin B12.
Beneficial features vitamin B12Vitamin B12 promotes the formation of red blood cells, in which the maturation of DNA molecules (deoxyribonucleic acids) occurs - substances in the cell nucleus that contain genetic information. DNA synthesis without vitamin B12 is not possible, and the information needed to form red blood cells is not transmitted. This leads to the occurrence of a disease such as pernicious anemia.
Another equally important function of vitamin B12 is the production of nerve cells. The covering of the nerves is the myelin sheath. When the body does not have enough vitamin B12, this coating begins to suffer, leading to gradual demyelination and death of nerve cells. The role of vitamin B12 in this process has been demonstrated many times to be effective in relieving painful and various other symptoms of the nervous system. Neurological pathology, as a rule, is accompanied by impaired neuromuscular motility and tingling in the extremities. This makes it clear why vitamin B12 is needed for the body.
Vitamin B12 affects the absorption of proteins. Most of the key components of protein, called protein, will become unavailable for utilization in the absence of vitamin B12. In addition, a lack of this vitamin will disrupt carbohydrate-fat metabolism in the body.
Numerous studies have shown that vitamin B12 plays an active role in education bone tissue. To a large extent, it is necessary for normal growth and physical development children.
Vitamin B12 in sufficient quantities is also good for hair. Being the main foundation for the construction of hair cells, this vitamin helps improve their reproduction, regenerate damaged tissue - brittle and split hair, prevent hair loss, improve growth, and normalize blood circulation, making curls shiny and beautiful.
What vitamin B12 is needed for and what its role is for the body is clear. But it is worth noting that its deficiency can lead to nervousness, depression, poor blood clotting, numbness in the legs, weakness, decreased reflexes, pale skin, difficulty swallowing, inflammation and redness of the tongue, rapid heartbeat, disruption of the normal functioning of the liver, problems with memory and menstrual irregularities.
 Sources of vitamin B12
Sources of vitamin B12
To ensure that your body does not lack vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin), you need to know which foods contain vitamin B12. It is important to include animal products in your daily diet, as they contain it in sufficient quantities. Excellent sources of vitamin B12 are veal liver and perch. Also present in the kidneys a large number of vitamin A. Salmon, scallops, halibut, sardines and cod are rich in it. Meat products include lamb, beef, and game. To enrich the body with vitamin B12, do not neglect kelp, blue-green algae, brewer's yeast, soy products - tempeh, miso and tofu.
It is very useful to take B12 in tablets or ampoules, which can be purchased at the pharmacy. The solution in ampoules is administered intramuscularly: 1 ampoule daily for 10 days. The tablets are taken orally after meals: 2 tablets per day for the same 10 days. This is especially important for people who follow a vegetarian diet.


