Among the many serious diseases digestive system in children, pathological changes in the pancreas are isolated, which are called "reactive". Their peculiarity lies in the fact that they are secondary in nature and represent nothing more than a reaction to other manifestations and diseases. To have an idea of what reactive changes in the pancreas are, you should know what this organ is, what functions it performs, as well as what disorders can occur and what causative factors they can be caused by.
The pancreas is an important organ of the digestive system, located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It consists of two types of fabric, each of which performs its task. The main purpose of the pancreas is to perform two functions:
- endocrine;
- exocrine.
The pancreas consists of small lobules, which in medical terminology are defined as acini. Each of them is endowed with an excretory duct. They are interconnected and discharged into one duct running along the entire length of the gland, from the head to the tail of the organ. The duodenum connects with the bile duct, opening from the right edge of the head. Between the lobules are the so-called islets of Langerhans. They do not have ducts, but are endowed with blood vessels, through which insulin and glucagon are released into the blood. The size of each island in diameter varies from 100 to 300 µm. Organ dysfunction, including reactive changes in the pancreas, is a potential danger to the child's body, since this organ is associated with the entire digestive system and is responsible for the release of pancreatic juice. It contains digestive enzymes that ensure high-quality digestion of food. As for the endocrine function, it is due to the production of hormones and the exchange of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the body. Any change in the pancreas in a child entails the development of certain consequences and requires a timely response.
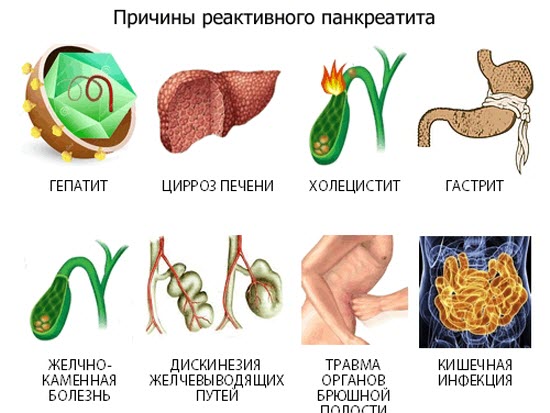
Causes of reactive changes in the pancreas in a child
Reactive changes in the pancreas in a child have their own causes, just like any other pathological processes of the digestive tract. These phenomena can be repeated and are caused by the presence of other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which are caused by improperly organized nutrition, the abuse of fatty, fried and spicy foods, excessive coffee and chocolate, as well as the development of intestinal infections.
 The reactive state of the pancreas is not specific, which is why the determination of its main symptoms requires laboratory tests. Similar pathologies in both children and adults have a different character. Somewhat less common are reactive changes in the pancreatic parenchyma, accompanied by an acute course and characterized as diffuse. As a rule, they arise as a result of anomalies, the development of which occurred during the formation of the organs of the digestive system.
The reactive state of the pancreas is not specific, which is why the determination of its main symptoms requires laboratory tests. Similar pathologies in both children and adults have a different character. Somewhat less common are reactive changes in the pancreatic parenchyma, accompanied by an acute course and characterized as diffuse. As a rule, they arise as a result of anomalies, the development of which occurred during the formation of the organs of the digestive system.
Diffuse changes in the pancreas of a reactive nature can develop against the background of the following pathologies:
- complicated forms of cholecystitis;
- ulcers of the stomach, duodenum or pancreas;
- ailments caused by reflux;
- colitis.
It should be borne in mind that the main symptomatology of structural changes in the organ, the cause of which was the reactive state of the pancreas in a child, however, as in an adult, is slightly expressed. This fact to some extent complicates the diagnosis, which involves the introduction of additional appointments during the examination, namely: clinical analyzes urine and blood.
Reactive changes in the pancreatic parenchyma can be caused by infectious diseases, which are often accompanied by an active inflammatory process. Among them are:
- pneumonia;
- pharyngitis;
- flu conditions;
- inflammation of the digestive tract;
- lesions of the abdominal organs;
- stressful situations;
- and a number of others.
In addition to the above, the causal factors are often improper catering, the use of canned foods, not diet meals, carbonated drinks, as well as treatment with certain medications, which include antibiotic diuretics.
The cause of pathological processes in the pancreas is also distinguished by congenital anomalies, which include a decrease in hormone levels, damage to the bile ducts, and cystic fibrosis.
Symptoms of diffuse changes in the pancreas
Reactive changes in the pancreas in an adult, as well as in a child, have their own symptoms. Among these signs are:
- the occurrence of pain in the stomach. A decrease in pain in this scenario can be observed during the adoption of a sitting posture. The occurrence of pain in a child is evidenced by restless behavior, and sometimes even crying;
- bouts of nausea, often accompanied by vomiting. Vomiting of gastric juice and undigested pieces of food with such symptoms does not bring relief to patients;
- an increase in body temperature, which can vary from 38 to 40 degrees. This usually happens at the beginning of the disease;
- violation of the chair, expressed in the occurrence of constipation, followed by bouts of diarrhea;
- dryness of the tongue and mouth, accompanied by the appearance of white plaque;
- loss of appetite;
- belching;
- flatulence;
- increased weakness.
Diffuse changes in the pancreas in a child can be expressed quite weakly. This state of affairs complicates the diagnosis even for a qualified specialist.
What is reactive pancreatitis
Parts of the pancreas, as well as the expansion of the ducts of the organ and the presence of diffuse tissue changes at the cellular level.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
A reactive change in the pancreas in a child may be due to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. In this case we are talking about such a serious pathology as a duodenal ulcer. It is worth noting that the pancreas has a close relationship with this organ: through the duct located in the intestinal wall, pancreatic juice and bile enter the intestine.
Somewhat less often, activation of inflammation occurs during pathological processes in the large intestine, with pathologies such as ulcerative colitis, gastric gastritis and other diseases of the esophagus accompanied by inflammation.
Diffuse changes in the pancreas in a child disappear with the restoration of all organs of the digestive system that have been affected. In other words, first of all, it is necessary to get rid of the causative factors, that is, to cure the disease that acts as a provocateur of similar manifestations.
inflammatory processes and infectious diseases do not go unnoticed. After them, children may suddenly develop reactive pancreatitis. In this condition, one organ of the digestive system is affected - the pancreas.
The development of reactive pancreatitis in children is evidenced by pain in the abdomen. However, this symptom occurs not only with inflammation of the pancreas, but also with other diseases. If your child complains of pain, see a doctor immediately. Do not start treating the baby yourself, because you will not be able to correctly diagnose.
In this condition, the child has a malfunction in the functioning of the pancreas. It covers the inflammatory process. Enzymes that are produced in the gland do not enter the duodenum and do not take part in digestive process, they remain in the body. Under the influence of enzymes, the pancreas begins to break down.
The causes of reactive pancreatitis can be childhood infections . Quite often, the pancreas becomes inflamed due to SARS. Symptoms of the disease also occur due to congenital pathologies. The organs of the digestive system, and even the pancreas itself, may have an irregular structure. Some pathologies prevent the release of enzymes, resulting in inflammation.
Reactive pancreatitis in a child sometimes occurs due to taking strong antibiotics, abdominal trauma . Plays a huge role food . Almost all children love fast food, chips, soda, chewing gum. These foods are harmful to health. The causes of inflammation of the gland can also be attributed to the uneven functioning of the digestive system (too much time between breakfast, lunch and dinner), poisoning.
Signs of reactive pancreatitis
Before talking about the symptoms of inflammation of the gland, it is worth noting that they are less pronounced in babies. Some signs may not be present at all. In adult children, the symptoms are clearly expressed.
The presence of reactive pancreatitis may indicate:
- frequent vomiting, after which there is no relief;
- yellow color of the skin;
- dark urine;
- too light feces;
- increased body temperature;
- crying and screaming, loss of appetite in newborns and infants.

The main symptom of the disease is intense pain that occurs suddenly and is localized in the upper abdomen. Young children cannot show where they have discomfort, as they feel pain around the navel or throughout the abdomen.
The first actions of parents and doctors
If a child has signs of reactive pancreatitis, then you should immediately call a doctor. Before his arrival, the baby should be provided with complete rest. The arriving specialist will examine the patient, listen to his complaints or ask the parents to tell about the condition of the young patient. The following studies are also being carried out:
- general analysis blood to confirm the presence of an inflammatory process;
- a biochemical blood test to determine the level of pancreatic enzymes;
- Ultrasound (ultrasound) or CT (computed tomography) of the organs located in the abdominal cavity to detect compacted areas of the pancreas, replaced by connective tissue;
- laparoscopy to clarify the form and type of the disease.
A child in serious condition with a diagnosis of pancreatitis must be hospitalized. Treatment is carried out conservatively. Surgical intervention is not required. The main principles of the treatment of reactive pancreatitis include the elimination of the causes of the disease and the use of medications to get rid of the existing symptoms: pain, vomiting, etc.
For a young patient, the doctor will prescribe medicines:
- Pirenzepine or other medicines with a similar effect (drugs that reduce the volume of gastric juice produced and inhibit the pancreas);
- Festal, Pancreatin - means that reduce pain and improve digestion;
- No-shpa, Platifillin (antispasmodic drugs that relieve pain and improve the outflow of pancreatic juice);
- glucose solution (to replenish the body with easily digestible nutrient material).
Often the specialist prescribes other medicines. The choice of drugs for the treatment of reactive pancreatitis in children depends on the specific situation.
Diet for inflammation of the pancreas
When a child develops a disease, parents should pay attention to his nutrition. The baby will have to follow a diet. Here are the main rules of nutrition for reactive pancreatitis:
- Providing the pancreas with functional rest. From the diet of the child, first of all, it is necessary to exclude irritants. Food cooked or steamed should be served chopped and warm. Even during remissions, young children (up to 3 years old) need to grind food, because at this age they do not chew it well.
- Preservation of the energy and nutritional value of the diet. When diagnosing reactive pancreatitis in a child, parents should not give their child only those foods that contain a lot of proteins. The diet should also contain other foods that contain the required amount of carbohydrates and fats. It is only necessary to use the most suitable products as sources of these components.
- Fractional nutrition. With reactive pancreatitis, you need to eat food not according to the usual pattern (breakfast, lunch and dinner), but in small portions at least 5-6 times a day. The interval between meals should not exceed 4 hours.

Features of nutrition in reactive pancreatitis
| day of treatment | Approved Products | Prohibited Products |
| 1st day | warm drink ( mineral water without gas) |
|
| 2nd day | ||
| 3rd day | tea without sugar with croutons made from lean dough without seasonings, oatmeal and buckwheat pureed porridge | |
| 4th day | fermented milk products (yogurt, fermented baked milk, kefir, cottage cheese, curdled milk), jelly and yesterday's white bread | |
| 5th day | vegetable purees or soups | |
| 6th day | ||
| 7th day | ||
| next week | it is allowed to supplement the diet with fish, boiled meat of low-fat varieties (veal, chicken), steam cutlets, and a little later you can introduce fresh fruits, vegetables and berries into the diet |
Exacerbations of reactive pancreatitis in children can be avoided, provided that even during remissions, prohibited foods are not included in the diet. Any experimentation with food can lead to a new attack and the need to follow a strict diet.
Prevention of reactive pancreatitis
If a child has already been diagnosed with inflammation of the pancreas, then in the future an exacerbation may occur again. Prevention helps prevent seizures. Parents:
- you should definitely watch what foods their baby uses;
- it should be remembered that in children's educational institutions (kindergartens, schools) food is dietary, but it does not correspond to the diet that must be followed with reactive pancreatitis;
- care must be taken to ensure that medical card a child for an educational institution was indicated the diagnosis and the need for special nutrition;
- if in educational institution there is no health worker, you can talk to the caregiver or teacher and give him a list of foods that the baby should not eat.
Not always parents can save from situations that provoke the occurrence of reactive pancreatitis in a child. The kid in the future will attend the birthdays of his friends, various holidays. That is why it is necessary to explain the seriousness of the disease to the child himself and inspire the need to follow a diet.
All children have a sweet tooth. However, it is cakes and pastries that cause swipe on the pancreas, because they contain both fat and sugar. One of the preventive measures reducing the consumption of sweets to a minimum . Honey can be an excellent substitute for cake and pastries, but here you should not overdo it. The child will be enough for 2 tbsp. l. this product. One more thing important rule- do not overeat. The child should get up from the table with a slight feeling of hunger.
An equally important preventive measure is timely elimination of infections , treatment of inflammatory processes and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. It is because of various ailments that children develop reactive pancreatitis. Only due to the timely treatment of diseases can self-destruction of the pancreas be avoided. At the same time, it must be remembered that it is impossible to prescribe any drugs to the child on their own.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that reactive pancreatitis in children is a rather dangerous condition. When the first signs appear, you should immediately seek help from specialists. If this requirement is ignored, the pancreas will gradually break down under the action of its own enzymes. Destructive changes in this organ are fraught with very serious consequences. For example, due to an untimely visit to a doctor, a child may develop diabetes mellitus in the future, and surgery may be required to remove part of the organ. Be attentive to your child.
Informative video about proper nutrition for children and parents
I like!
The pancreas performs two main functions at once - endocrine and digestive. It is associated with many organs in the body. When one of the organs of the body fails in the implementation of its functions, reactive changes in the pancreas occur.
The concept of "reactive state" often causes panic fear in patients. However, this only means that the digestive organ located close to the gland does not perform its functions well.
These reactive changes in the pancreas can be accompanied by pain, increased blood sugar, and poor digestive function.
When the pancreas fails, there is an increase in the volume of pancreatic juice, its outflow is disturbed, enzymes cease to be produced in sufficient quantities, and the gland begins to digest itself.
Inflammatory processes have the following symptoms:
- Reactive changes in the pancreas.
- Swelling of the organ, an increase in size.
The progression of reactive changes in the pancreas can lead to serious complications, such as:
- cholecystitis;
- the formation of cysts and stones;
- hepatitis.
Symptoms of reactive changes:
- nausea, bouts of vomiting;
- pain in the upper abdomen;
- diarrhea.
Carrying out diagnostics
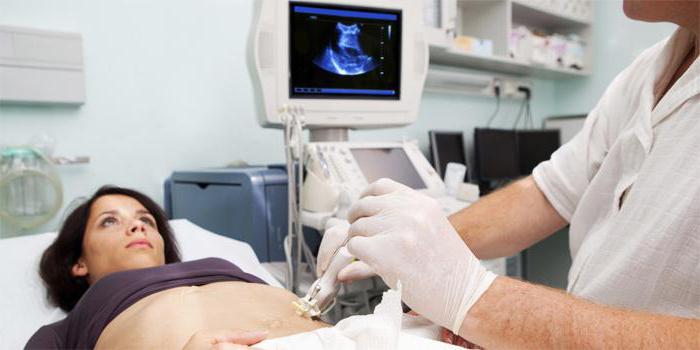
Changes in the pancreas can be diagnosed using an ultrasound examination. All organs of the digestive system are subject to examination. In order to find out what could be the cause of this condition.
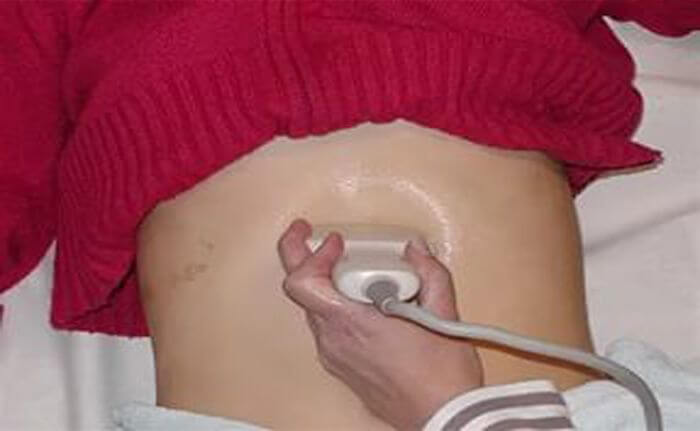
When examining a healthy pancreas, the picture is as follows: the dimensions correspond to the norm, there are no inflammatory foci, and there are also no diffuse changes in the pancreas.
Diffuse changes are foci of inflammation that are distributed throughout the organ and are most often associated with the presence of stones or tumors.
In addition to ultrasound, studies, the patient must additionally undergo examinations:
- a blood test to detect an inflammatory process;
- urine test for the presence of digestive enzymes;
- endoscopy of the duodenum.
After passing all the tests, the gastroenterologist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate effective treatment.
Reactive state of the gland in a child
Reactive changes in the pancreas in a child are a frequent occurrence, which is associated with a large number of harmful environmental factors. For example, as: the use of foods containing dyes, preservatives, carbonated drinks, crackers, chips, etc. Basically, the disease manifests itself in the form of spasms of the ductal gland.
The pancreas in children is susceptible and changes can occur for various reasons:
- with frequent colds, and a consequence of taking antibiotics;
- eating "harmful" foods;
- congenital pathologies of the gland;
- transferred stressful situations.
With reactive pancreatitis, a child has the following symptoms:
- sharp fights in the stomach;
- nausea, vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- dry mouth;
- the appearance of a white coating on the tongue;
- irritability, crying, whims.
Treatment
First of all, it is necessary to treat the manifestation of the first symptoms. Get rid of the pain, give the child sorbents and more fluids to alleviate the condition with vomiting. In order to prevent dehydration of the child's body, it is necessary to give a saline solution, which can be prepared independently at home or bought ready-made at a pharmacy.
Eliminate completely harmful products, fatty foods, carbonated drinks. After providing first aid and alleviating the condition of the child, it is necessary to call a doctor who will prescribe the necessary examinations, as well as taking medications.
Diagnosis of a child's body is similar to an adult examination:
- biochemical and general blood test;
- analysis of feces and urine;
- Ultrasound of the digestive organs;
- x-ray of the gastrointestinal tract.
Medical therapy
Treatment of the pancreas in children should be carried out in a hospital under the supervision of medical personnel.
You need to eat in small portions, but often. Useful fasting during the first two days in order to give rest to the gland.
With reactive pancreatitis in children, the following should be removed from the diet:
- sweets;
- soups in meat broth;
- canned foods, as well as any with the addition of spices and spices;
- fresh vegetables and fruits that have not undergone heat treatment.
Diet is necessary in order to avoid secondary changes in the gland in the future.
Medical therapy
The doctor may prescribe drug treatment which includes taking the following medications:
- glucose to remove toxins from the body. It is administered intravenously as oral administration is prohibited for several days;
- drugs to reduce the production of pancreatic juice;
- enzymes to relieve pain and improve digestion;
- antispasmodics to reduce pain and spasms.
It is important to remember that reactive changes are not a diagnosis, but only a manifestation of organ malfunctions in the body, an alarm signal about disorders of the digestive system. As soon as the functions of the diseased organ are restored, there will be no trace of reactive states.
The echogenicity of the parenchyma of a healthy pancreas on ultrasound is similar to the echogenicity of the liver and spleen. In its structure, the gland has a head, body and tail of optimal sizes. Unfortunately, people who already have problems turn to specialists, and on the monitors of diagnostic devices, signs of diffuse changes in the pancreas are often observed due to its inflammation or other pathology.
About diffusion
The term "diffusion" in Latin means "spreading" or "interaction". From the point of view of physics and chemistry, this is the penetration and interaction of atoms or molecules of one substance with atoms and molecules of another. Studying the phenomenon of diffusion, scientists began to better understand the essence of the processes occurring in the human body. This is most often the case with the pancreas. Diffuse changes - what is it?
It is easy to observe this phenomenon. It is enough to add a little ink to a glass of water and see how the substances mix. In anatomy, this phenomenon is associated with the interaction and replacement of some cells by others. This is exactly what is detected by ultrasound: pathologically altered cells are located next to healthy ones. Signs of diffuse changes in the pancreas, as a rule, are local (focal) or mixed (diffuse).
What are diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma?
Pathogenic changes in the tissue of the gland are most often chronic, and therefore there are no symptoms. But on ultrasound, with normal sizes, the echogenicity of the gland is increased. In elderly patients suffering from cardiovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, healthy cells gradually die off, they are replaced by connective or adipose tissue.
Also, such transformations are observed in violation of the blood supply to the enzyme-forming organ, the liver, in violation of the functioning of the biliary tract, in violation of endocrine and metabolic processes. In what other cases do diffuse changes in the liver and pancreas occur?
Similar symptoms are observed with pancreatitis or dystrophic disorders of the metabolic process. The diagnosis of "pancreatitis" may not be confirmed, and then treatment is not prescribed, and the patient is not recognized as DIGI. As a rule, spreading changes occur in the chronic course of diseases, pathogenic tissue changes are almost asymptomatic. These are moderate diffuse changes in the pancreas.
Provoking factors
The disease can be triggered by various reasons:
1) Imbalance in nutrition. Abuse of fatty, floury, salty, sweet and spicy foods.
2) Predisposition along the genetic line.
3) Stress and nervous strain.
4) Drug and alcohol addiction.
5) Chronic diseases of the digestive system.
6) Self-medication and indiscriminate use of drugs.
How to treat diffuse changes in the pancreas? Let's look at it below.
Insufficient amounts of insulin in the blood and the detection of glucose in the urine are also provoked by DIGI. As a rule, the cause of these changes is pancreatitis, which must be treated. It is necessary to comply certain rules patient behavior, diet.
The main signs of diffuse changes in the pancreas
As a rule, the signs of DI are associated with the underlying disease. Most often, patients complain that they feel heaviness in the stomach, they suffer from frequent diarrhea or, conversely, constipation. In acute pancreatitis, pressure in the pancreatic duct often increases, which can cause its deformation. Due to a violation of the enzymatic function, part of the digestive enzymes can pass through the cells of the pancreatic parenchyma and cause poisoning of the body. In this case, the patient experiences pain on the left under the sternum, nausea, often accompanied by vomiting. There is a rapid pulse and low blood pressure. This condition usually requires hospitalization.
The initial stage is accompanied by the appearance of edema and hemorrhages in the tissues of the gland. Then atrophy sets in, the gland decreases in size, the connective tissue grows, and the enzyme-forming cells stop producing digestive enzymes. Fibrosis is also accompanied by displacement of healthy pancreatic cells and their replacement by connective tissue. The production of hormones and enzymes stops. Initially, symptoms are mild and often mimic signs of pancreatic inflammation. There are moderate diffuse changes in the pancreas.
About lipomatosis
The replacement of normal organ cells with adipose tissue is called lipomatosis. The symptomatology of DIP with lipomatosis depends on its volume. With minor changes in CI, the pathology may not manifest itself, however, in more serious cases, the body begins to gradually experience a deficiency of hormones and enzymes. The proliferation of lipoid tissue leads to compression of the parenchyma and, as a result, disruption of the functioning of the pancreas and the appearance of pain. These are diffuse changes in the pancreas by the type of lipomatosis.
Hollow organs include: stomach, urinary and gall bladders. Organs consisting of parenchyma (glandular tissue): pancreas, spleen, liver, etc. The main function of the pancreatic parenchyma is the production of enzymes and hormones.
With diabetes mellitus, or acute pancreatitis, there are often changes.
On ultrasound, an increase in the echogenicity of the glandular tissue is noted, this occurs due to the inflammatory process and when the connective tissue coarsens (fibrosis), which leads to an increase in density. The reason for this anomaly is an imbalance in metabolism. Another reason for the increase in echogenicity is lymphomatosis (replacement of the parenchyma with fat cells).
Puffiness of the gland can occur due to pancreatitis, due to which the density of the parenchyma changes and, as a result, the echogenic reaction also changes.
How do diffuse changes in the parenchyma of the liver and pancreas affect the state of the organs?
Structure changes
The structure of the parenchyma can be homogeneous and fine-grained. Slightly increased graininess is also not a big deviation. Taken together, an increase in granularity indicates the presence of inflammation and dystrophic changes in the gland associated with malnutrition.
A healthy parenchyma of the pancreas resembles the echostructure of the liver, the same homogeneous and fine-grained. Age-related changes in the echogenicity of the structure of the gland indicate developing lipomatosis, which is often associated with the onset of diabetes. Signs of diffuse changes in the pancreas can be very informative.
Reactive DIPs
These are its secondary changes, a response to pathology in neighboring digestive organs, closely related to it. Especially often, DI glands occur due to problems with the liver and biliary tract, as it interacts most closely with these organs. On ultrasound, reactive echo signs of diffuse changes in the pancreas resemble acute pancreatitis, since they are most often its secondary consequence.
Fibrous DIGI
Fibrotic DIs are scarring in the connective tissue gland that spreads through the cells of the tissue. The reasons for this process are often:
1) Metabolic disorders.
2) Alcohol poisoning.
3) Viral lesions.
4) Inflammatory processes.
Moreover, the lesions caused by viruses concern the entire hepatobiliary system, and not just the pancreas. On ultrasound, diffuse changes in the pancreas have high echogenicity and density. The presence of diffuse fibrous changes may indicate an existing benign tumor of the glandular tissue - fibroma, the growth of which can compress the gland and cause pain.
Depending on the location of the fibroma, different symptoms will be present. For example, when it is in the head of the pancreas, the flow duct is clamped, and a symptom of jaundice occurs. If the tumor presses on the duodenum, nausea, vomiting and other symptoms occur that require differentiation from intestinal obstruction. What other echo signs of diffuse changes in the pancreas are there?
Dystrophic DIPG
There is a replacement of healthy glandular cells with fatty tissues that are unable to perform the enzymatic function of the pancreas, which leads to hypofunction of the gland. For lipodystrophy, which occupies less than half the volume of the entire gland, mixed drug treatment is used in conjunction with a diet. If the lesion covers more than half of the organ and its work is impaired, surgical intervention is indicated. Diffuse changes in the parenchyma of the liver and pancreas in some cases are life-threatening.
In the structure of this secretory organ, three elements are distinguished: the body, the head and the tail, which is pear-shaped and adjacent to the spleen. Normally, its width is 2-3 cm. An excretory duct about 15 cm long passes through the entire gland. Blockage of the hepatic vein can lead to DI of the tail of the pancreas, the symptoms of this are that this part is thickened.
Approximately a quarter of all pancreatic diseases are associated with diffuse changes in the tail. In case of minor lesions of the tail, they are treated with conservative methods. In the case of deep lesions, removal of the tail is indicated, followed by occlusion of the blood vessels.
How are diffuse changes in the liver and pancreas detected?
Diagnostics
DIGI are determined by ultrasound. Ultrasound reveals that the density and structure of the tissue are changing, foci of inflammation are determined.
But this is not enough to make a diagnosis. To confirm the CI, a biochemical blood test and endoscopy of the gland are performed. It is very important to correctly collect an anamnesis from the patient (a survey about the presence of complaints), as well as conduct additional instrumental studies and palpation.
The overall picture is complemented by a general blood test, urine, endoscopy of the gastrointestinal tract, coprogram, etc. Pancreatic enzymes and blood glucose, as well as an inhibitor in relation to trypsin, play an important role.
With the help of ultrasound, the size of the gland and its ducts are determined, neoplasms and seals are detected. To clarify the diagnosis, the following are shown: computed tomography and ERCP, which make it possible to more accurately identify the causes of the changes that have occurred in the tissues of the enzyme-forming organ. Diffuse changes in the pancreas by the type of lipomatosis are most clearly manifested.
Prevention
The process of development of DI in the pancreas, liver and other organs can be slowed down. Here are some rules:
1) It is necessary to completely abandon alcohol.
2) Follow a diet, take food in small portions, but often.
3) Minimize the consumption of fatty foods.
4) Refuse canned foods.
5) Drink freshly squeezed juices and drink herbal teas.
You should not give up if you have been diagnosed with PDIP. It’s just worth going through the necessary studies and in the future carefully listening to your body, monitoring the health of such important organs as the liver and pancreas. Diffuse changes, what they are and what are the methods of treatment, we examined in the article.
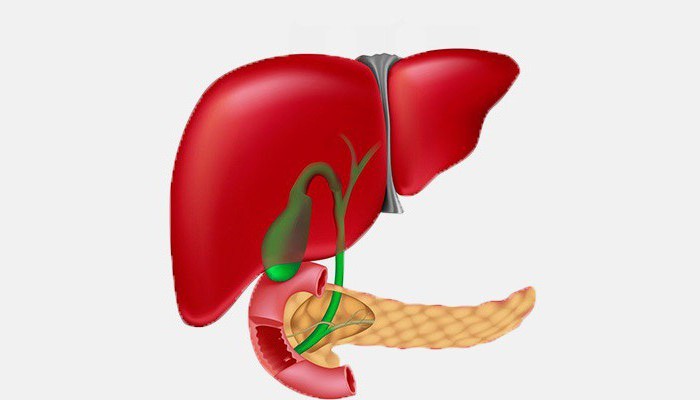
The term "reactive" means secondary, that is, it is the reaction of the body to some other disease. The pancreas can give reactive changes to any disease of the digestive system, since the functions of all these organs are interconnected. But the pancreas has the closest connection with the liver and bile ducts.
What is reactive pancreatitis
Reactive pancreatitis can develop in patients with any diseases of the digestive system, with constant overeating and eating fatty fried foods, some congenital enzymatic disorders, with prolonged use of certain drugs (for example, glucocorticoids), abnormal development of the biliary tract.
On ultrasound, you can see the same changes as in acute pancreatitis: an increase in one of the sections of the pancreas (usually the tail), expansion of the pancreatic duct, diffuse changes in the pancreatic tissue.
Diseases of the liver and biliary tract
For liver diseases  and biliary tract almost always appear reactive changes in the pancreas. This happens because these organs are interconnected by a common duct, into which the common bile duct and the pancreatic duct are combined.
and biliary tract almost always appear reactive changes in the pancreas. This happens because these organs are interconnected by a common duct, into which the common bile duct and the pancreatic duct are combined.
With stagnation of bile in the bile ducts and in gallbladder reactive changes appear in the pancreatic tissue, which the ultrasound doctor sees and describes. These changes are always diffuse (common) in nature, but are often found in one of the areas of the pancreas. Such reactive inflammation indicates a close connection of organs.
The same thing happens with liver diseases (acute and chronic hepatitis), when its function of producing bile by liver cells is disrupted.
Such reactive changes often do not manifest themselves in any way or their symptoms are insignificant. Pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, and loose stools periodically appear. But since such symptoms can also appear in diseases of the liver and biliary tract, it is sometimes impossible to distinguish the symptoms of liver and biliary tract disease from the symptoms of reactive changes in the pancreas.
Reactive changes in the pancreas do not require special treatment. This condition disappears after recovery from the underlying disease or after its exacerbation has passed.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Reactive changes in the pancreas can also develop in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. So, quite often, such reactive inflammation develops during exacerbation of duodenal ulcer. The pancreas has a close connection with the duodenum, since a common duct opens in its wall, through which bile and pancreatic juice enter the intestine. This reactive inflammation can lead to increased and upward radiating abdominal pain, nausea, loose stools, and bloating.
Sometimes there is a penetration (spread) of the ulcer of the stomach and duodenum into the head of the pancreas. In this case, reactive inflammation of the pancreas increases.
Less commonly, reactive inflammation of the pancreas occurs with diseases of the large intestine, such as ulcerative colitis.  and in diseases of the esophagus. Reflux can lead to reactive inflammation of the pancreas
and in diseases of the esophagus. Reflux can lead to reactive inflammation of the pancreas  -gastritis - inflammation of the esophagus, which occurs against the background of the constant leakage of the acidic contents of the stomach into the esophagus. Such constant irritation leads first to inflammation, and then to the formation of ulcers on the walls of the esophagus - a serious disease that affects the state of all digestive organs, including the state of the pancreas.
-gastritis - inflammation of the esophagus, which occurs against the background of the constant leakage of the acidic contents of the stomach into the esophagus. Such constant irritation leads first to inflammation, and then to the formation of ulcers on the walls of the esophagus - a serious disease that affects the state of all digestive organs, including the state of the pancreas.
Reactive changes in the pancreas pass with the restoration of the normal state of the organs that caused it.
Is additional research needed?
As a rule, they are carried out, since it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based on one ultrasound. With reactive changes in the pancreas, its function is slightly impaired. If it is found in the blood and urine a large number of pancreatic enzymes, then concomitant treatment is prescribed.
With reactive changes in the pancreas, you need to look for some kind of disease of another digestive organ.
Galina Romanenko