To keep the blood in a liquid state, 2 systems are counteracted, namely coagulation and anticoagulation. With the help of these mechanisms, coagulation homeostasis occurs. Platelets play a huge role in coagulation, life expectancy, their role - such questions often worry people.
Content:
What are platelets and what is their life cycle?
Without blood, a person cannot exist; it is plasma in liquid form. It contains shaped elements. These perform the necessary functions of the blood.
An important part of the blood are platelets. These are cells small sizes and spherical shape. Their diameter is ten times smaller than a hair. They have a specific life cycle, which begins with the bone marrow. This is where platelets are produced.
The precursor of these cells is the megakaryocyte. It takes more than a week for it to transform into a mature platelet. Platelets are then released from the bone marrow into the bloodstream. At the same time, there are both mature ones and those who have not yet had time to ripen. If there are a lot of the latter, then blood clotting will be impaired.
Platelets that have entered the bloodstream will still have their functions for 11 days. They gradually lose mobility and stop secreting a certain substance that makes it possible to move along.
They often accumulate in reticular tissue, namely the liver and spleen, where they are destroyed. As a result, some substances and proteins are formed that are subsequently necessary for the creation of new platelets.
Normally, a person’s blood should have 150-400 thousand cells, which are located in 1 ml. This figure varies and is influenced by gender, age, and health status.
These cells are necessary to perform the following functions:
- The most important thing is that platelets are able to create a plug when the vessels are damaged. For example, if a person cuts himself, then these cells will lie down in order to close the cut and stop the bleeding.
- They help blood clot, which is also necessary to stop bleeding in case of injury.
- Platelets provide nutrients for certain vascular cells.
Considering these functions, we can conclude that deviations from the norm can be dangerous. After all, when platelets decrease, the vessels do not receive the necessary nutrition, and if it appears, it will be difficult to stop it
Causes of high or low platelets in the blood

To determine how many platelets are in the blood, a person should have their blood tested. After this, specialists carry out the verification procedure using a microscope or new automatic instruments. But any analysis will require blood, which is taken from a finger.
In some cases, some deviations from the norm may be detected. The platelet count may be increased or decreased. Such deviations may indicate some kind of disorder in the body.
An increased platelet count is called thrombocytosis in medicine. This is influenced by the following reasons:
- Development of erythremia, myelofibrosis
- The emergence of diseases associated with inflammatory processes
- Development of tuberculosis, liver cirrhosis, ulcerative colitis
- The occurrence of a malignant formation
- The appearance of bleeding or
- Thrombocytosis may appear after megaloblastic anemia while the person is recovering
- In the postoperative period
- When are corticosteroids used for treatment?
- When a person has had a splenectomy
There are situations when the platelet count decreases. This phenomenon is called thrombocytopenia. This is influenced by the following reasons:
- Heredity, which provokes a decrease in the appearance of platelets.
- Blood diseases. This could be aplastic anemia, leukemia.
- For disorders in the bone marrow. For example, tuberculosis, tumor metastasis, previous radiation.
- Kidney failure, liver disease, neoplasms in blood vessels.
- Various that have entered the body.
- This change can be affected by menstruation or.
- Consequences from certain medications, alcoholic beverages, heavy metals.

Thrombocytopenia is dangerous phenomenon, as the risk of prolonged bleeding increases, since the blood will not be able to clot normally. But thrombocytosis does not pose such a serious danger, but it can provoke some complications. Therefore, you should not ignore the increased platelet count.
Symptoms of low platelet count, treatment
When the number of platelets in the blood decreases, a person needs immediate help. This is due to the fact that such a phenomenon poses a threat to human life. This deviation leads to the fact that the walls of the blood vessels become less elastic and can easily become damaged, which can lead to internal inflammation.
Even before a blood test, a decrease in platelet levels in the blood can be suspected. The person will have the following symptoms:
- Bruises easily without hard impacts
- Gums bleed when brushing teeth
- Bleeding from
- In women, menstruation is heavy and lasts a long time
- You may notice a rash in the form of small dots on the body
- Once a person cuts himself, it is difficult to stop the bleeding.
Thrombocytopenia can cause all or some of these symptoms. In order to detect deviations in time, you should systematically donate blood for analysis.
With such a deviation, the person feels familiar and there is no pain. But he needs immediate treatment. Otherwise, the disease can provoke serious bleeding of internal organs. Brain hemorrhage may also occur, which is especially dangerous.
Initially, when the disease was discovered, the doctor tries to determine the cause of such a deviation. This is done to prevent recurrent thrombocytopenia.
There are situations when treatment does not bring a positive effect. In this case, the patient’s spleen, which is the main hematopoietic organ, is often removed. Most patients recovered after this operation.

If a person has this disease, he should regularly visit a doctor to monitor his health. He should also adhere to the following recommendations:
- It is better to refuse sports activities that can bring.
- A person should exclude alcohol, canned food, and those dishes that contain vinegar from their diet.
- It is necessary to stop taking aspirin, analgin and other medications that interfere with platelet function.
- It is recommended to eat foods that contain A, P and C. This is especially useful for those who often have there's blood coming out from the nose.
Nutrition for thrombocytosis
When a person has been diagnosed with thrombocytosis, he is recommended to adhere to a certain diet. Namely:
- Every day you should eat food that thins the blood. This is olive oil, lemons, fish fat, tomato juice, onions and berries that taste sour.
- Garlic will be especially useful. Studies have been conducted that have shown that regular use of this product helps thin the blood and also eliminate blood clots that have formed.
- Products that contain magnesium prevent blood clots from forming. Therefore, they should also be included in the diet.
- A person should drink a lot of water. About 2 liters should be drunk per day. Also beneficial green tea, juices.
- But foods such as bananas, rosehips, pomegranates, and mangoes should not be eaten, as they thicken the blood.
- Negatively affects the blood condition alcoholic drinks, nicotine and some medications.
While watching the video you will learn about platelets.
So platelets are important element, which have a certain life cycle. For any deviations, treatment should be started. Otherwise, complications may arise.
Platelets are special blood cells that are fragments of individual cells called megakaryocytes. Elevated platelets in the blood, what does this mean and the causes of this phenomenon? In order to answer this question, first of all we need to understand what role platelets play in the body and why we need them at all.
The role of platelets in the body and the norm of their content
It’s hard to believe, but back in the middle of the last century, scientists knew quite little about platelets. Then their detailed structure was described by the Italian Bizzocero and science seriously began studying these simple, but such important components of blood. The platelets themselves are formed in the bone marrow; these are small pieces that break off from the cytoplasm of megakaryocytes and then enter the main bloodstream. But you shouldn’t think that this is some kind of “garbage” - nothing happens in the body for nothing.
The main property of platelets is their ability to stick together. They can stick together or settle on the surface of the blood vessel. It is platelets that play a major role in the ability of blood to clot. If even a small vessel is damaged, its walls begin to release special substances that accelerate the rate of platelet aggregation. As a result, platelets clump into a lump, which attaches to the wall of the damaged vessel and reliably clogs it, preventing the development of internal bleeding. Approximately the same picture is observed with any external damage. In other words, if there were no platelets, any wound or damage to the tissue or vessel could be fatal to the body, since it would lead to significant blood loss.
Platelets have a lifespan of about 10 days, after which they are deposited in the liver or spleen and then recycled. Meanwhile, more and more platelets enter the blood. It is by their content in the blood that one can judge how correctly the process of hematopoiesis occurs in the body and whether there are any violations in it.
In blood healthy person Normally there should be 180 - 320 x 109/l platelets. In newborn children, a few m may be slightly less or slightly more - 100 - 420 x 10 9 / l, this is completely normal. The platelet level in the blood of pregnant women also changes. Here they are usually contained 150 - 380 x 10 9 / l. But, as we see, all these changes are not too significant.
Elevated platelets in the blood, what does this mean and the reasons for their increase
In some cases, the hematopoietic processes in the body may be disrupted, and then, for example, the level of platelets increases compared to the normal norm. This can happen, for example, in the case of removal of the spleen, some acute infectious diseases, development of the inflammatory process and even iron deficiency in the body. This phenomenon is called thrombocytosis. If thrombocytosis occurs as a reaction of the body to a disease, it is called secondary, but if the number of platelets increases directly due to disturbances in the bone marrow itself, due to which it begins to intensively produce these blood cells, this is primary thrombocytosis.
Thrombocytosis is not at all harmless. Due to increased platelets, blood clots form in the blood vessels and can become completely blocked. Against this background, many different diseases are formed, for example, swelling of the extremities, ischemia, blockade of the veins of internal organs, vasoconstriction, erythema, heart attacks, and so on.
What to do if you have elevated platelets in your blood
If the result of a blood test shows an excess platelet count, then, as a rule, before making a final diagnosis and prescribing treatment, a repeat blood test is performed, approximately 4-5 days after the first. If elevated platelets continue to persist, the doctor should prescribe a number of additional tests, including a blood test for iron and ferritin levels, a general urinalysis, an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, and a C-reactive protein test.
Your doctor may prescribe an appointment to help lower your platelet levels. medicines blood thinners, such as aspirin, anticoagulants or other drugs. Remember that although many of them are sold in pharmacies without a prescription, this does not mean that you can start taking them yourself, without first consulting a specialist. On your own you can only use folk remedies, such as ginger, fresh nettle juice or sugar-free cocoa, which should be drunk in the morning on an empty stomach. You can also lower platelet levels by following a special diet. Enrich your diet with foods that help thin your blood. This - tomato juice, fish oil, garlic, olive and linseed oil, onions and foods high in magnesium. Try to drink as much liquid as possible throughout the day. Often the cause of thrombocytosis can be dehydration. This is especially true for people living in hot climates.
Here are the bananas walnuts, mangoes, pomegranates, and lentils are best excluded from the menu, at least for a while. You should also refrain from smoking and drinking alcohol.
However, in case of thrombocytosis, consultation with a doctor is still necessary. If only to determine what exactly was the cause of such a pathology and, if possible, eliminate it.
Blood is a complex organic substance, and platelets are its most important component. They play an important role in the body, performing a number of complex functions, participating in various processes. Deviation of the level of blood platelets from the norm is one of the signs of disease, which is why determining the number of these blood cells is used as a diagnostic method. Let's try to figure out what platelets are responsible for and what their role is in human life.
Platelets are non-nuclear components of blood that have an oval shape. The approximate size of platelets is 0.002 to 0.006 mm. The unique structure of platelets allows them to change shape. In a passive state, they have a disc-shaped shape, but when activated, they become rounded, and growths form on their surface.
The average lifespan of platelets is about 10 days. This is a fairly short period of time, which is why active formation of platelets constantly occurs to replace used ones. Platelet destruction occurs in liver cells or kidneys, which are a kind of filter for human blood.
With age, platelets are formed more and more slowly, which is associated with the gradual depletion of the body and a number of other factors. The bone marrow is the site of platelet production. The formation process takes place in hollow bones, for example, in the vertebrae, pelvic bone, and ribs.
The bone marrow produces stem cells, which initially do not perform any functions and are not divided into types. Subsequently, under the influence of certain organic substances, plaques are produced from each stem cell. They move freely through the bloodstream and, if there is no need for active functioning, are stored in the spleen.
If any pathological process occurs in the human body, under the influence of adrenaline, blood cells leave the spleen and move to the site of the lesion.
In general, platelets are the most numerous components of the blood and play a vital role in the body. To determine what platelets are needed for, it is necessary to become familiar with their functions in detail.
Functions
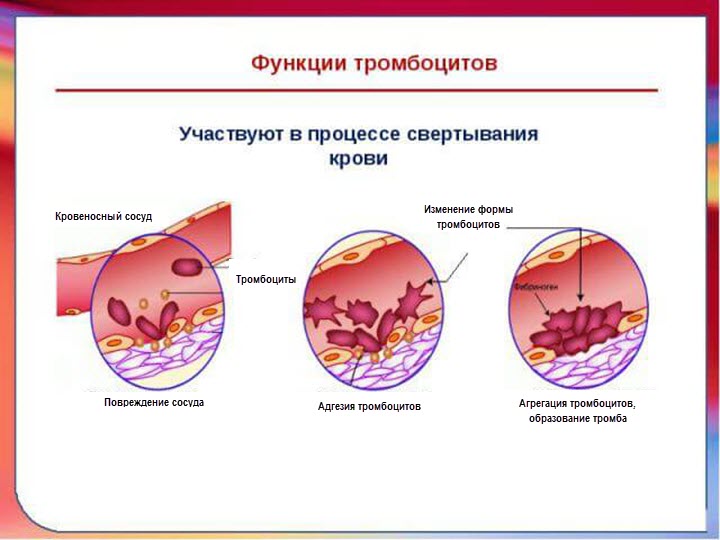
The significant importance of platelets in human blood is explained by their functions. The main property blood platelets is the ability to stop bleeding. When blood vessels are damaged, they a short time fall into the affected area and, connecting with each other, prevent heavy blood loss. In this way, the body protects itself from the loss of a large volume of organic fluid, and internal organs- from possible oxygen deficiency.
Stopping bleeding occurs in several stages:
- Early reaction. Having received a signal about any violation, the brain, with the help of adrenaline, releases the blood platelets located in the spleen, and also uses platelets in the blood. After this, they form a platelet plug, which prevents excessive blood loss.
- Release of substances. Once a plug is formed, the plaque releases several types of substances into the blood. They narrow the damaged vessel, thereby limiting blood circulation in the affected area.
- Secondary hemostasis. When blood loss slows down significantly, a fibrin clot forms. During this period, substances contained in the walls of the vessel are included in the healing process. This leads to the formation of a blood clot.
- Stop bleeding. Complete cessation of blood loss occurs when the fibrin clot thickens. Moreover, due to the fact that the life expectancy of platelets in humans is quite short, a signal is transmitted to the body about the need to produce new blood cells.
- The hemostatic functions of blood platelets are one of the body's natural defense mechanisms.
- In addition, platelets are responsible for the following functions:
- Accelerated growth. One of the structural features of blood platelets is the ability to accumulate biologically active substances. When a platelet dies or is destroyed under the influence of certain factors, the resulting substances enter the bloodstream and affect the growth of new cells.
- Tissue regeneration. Once in the place where the integrity of the vessels is damaged, some of the plates also disintegrate into their constituent components. In turn, they make the damaged vessel less sensitive to negative influence and accelerate the regenerative process.
- Immune protection. In addition to stopping bleeding, the main function of platelets is to protect the body from pathogenic microorganisms. The structure and functions of platelets include the ability to capture foreign objects and break down along with them.
Undoubtedly, the role of platelets cannot be underestimated, since they perform important protective functions and contribute to the normal functioning of the body.

Blood platelets: normal and abnormalities
A complete blood count is done to determine platelet levels. Normally, the concentration of blood platelets ranges from 200 to 400 thousand units/μl. This figure is an average and may vary depending on certain factors. For example, in pregnant people, the concentration of platelets, as well as the total volume of blood, increases significantly. Evidence of pathology can be either a decrease or an increase in the number of blood cells, which is reflected in a blood test.
Thrombocytopenia
Given the importance of the main function of platelets, a decrease in platelet production is considered more dangerous, because such a violation significantly affects the wound healing process. With minor tissue damage, bleeding stops on its own for a very long time or does not stop at all until special drugs are used for this.
What causes thrombocytopenia:
- Anemia.
- Viral diseases.
- Long-term use of antibiotics.
- Vitamin deficiency.
- Intoxication of the body.
- Diseases affecting the bone marrow.
- The influence of harmful substances.
Thrombocytopenia requires corrective therapy aimed at normalizing the concentration of blood cells. During the treatment period, the patient is recommended to move as little as possible and be at rest more often in order to prevent accidental injuries and resulting bleeding. It is prohibited to engage in any types of potentially hazardous activities.
Correction of the level of blood platelets is carried out by rationalizing nutrition, including in the diet foods containing enriched fatty acids, minerals, and vitamins. In this case, it is necessary to completely avoid high-calorie foods and alcohol. If the low platelet count is caused by a medical condition, appropriate drug treatment is prescribed.
Thrombocytosis
Thrombocytosis - accelerated production of blood cells - is also a pathology. Such a disorder can be an independent disease, but more often it acts as a symptom of another disease.
To determine why it is necessary to maintain the level of blood plaques within normal limits, it is necessary to remember their main function. With an increased level of platelets, increased formation of blood clots occurs, which interferes with normal blood flow.
If left untreated, the resulting blood clots impair the patency of blood vessels, causing atrophic processes in the tissues. In turn, this becomes the cause of a wide range of pathologies. The greatest danger is for the cardiovascular system and the brain, which can suffer as a result of a stroke caused by atherosclerosis due to thrombosis.
Causes of thrombocytosis:
- Hereditary disorders.
- Infectious diseases.
- High level of stress load.
- Previous surgical operations.
- Lack of iron in the body.
- Removed spleen.
- Inflammatory diseases.
Reducing blood plaque levels can be done different ways. The optimal method is selected by the attending physician in accordance with the diagnostic results.
In general, deviations in the number of plaques from established norms represent a pathological process that can occur against the background of various diseases. Such disorders require treatment due to the high likelihood of complications.
Platelets are an important component of the blood, performing a number of important protective functions. A detailed characterization of platelets allows one to obtain information about their basic properties, which is quite important for performing various diagnostic procedures.
Platelets are one of the main components of human blood. Experts recommend maintaining their levels at normal levels, otherwise the risk of fatal diseases increases. This is why it is so important to know what function platelets perform.
Basic Concepts
Platelets are round blood elements that participate in the normalization of hemostasis. The cells are microscopic in structure and do not have a nucleus. Their diameter is only about 3 microns. They are formed from megakaryocytes in the bone marrow. These elements remain in the bloodstream for 5 to 11 days. Then they are destroyed in the spleen and liver.
At rest, platelets have the shape of a rounded disk. At the moment of activation, they swell and become like a sphere. Since the main functions of platelets in the blood are to protect blood vessels, when cut, they form specific outgrowths called pseudopodia. With the help of these protrusions, the bodies attach to each other, that is, they enter the aggregation stage. The cells then adhere to the damaged area of the vessel. This ability is called adhesion. It is noteworthy that platelets are capable of releasing dozens of useful microcomponents into the blood, such as enzymes, serotonin, adenosine diphosphate, fibrinogen and others. This distinguishes them from other red cells.
Main function of platelets
As is known, these blood cells take an active part in the coagulation process, that is, in hemostasis. This is the main function of platelets. For the human body, this process is one of the most important. It helps prevent significant blood loss during serious injury.
Thanks to this function of human platelets, the walls of blood vessels become stronger. The corpuscles clog the injury site in a short time. In essence, these blood cells play the role of the primary vascular plug.  Coagulation occurs as a result of the interaction of enzymes, proteins and about 40 other components. This is a very complex biological mechanism in which main role platelets, prothrombin and fibrinogen play. The interaction of these elements occurs in
Coagulation occurs as a result of the interaction of enzymes, proteins and about 40 other components. This is a very complex biological mechanism in which main role platelets, prothrombin and fibrinogen play. The interaction of these elements occurs in
Auxiliary functions of platelets
Besides protective properties, these red plates have another useful ability. It consists in feeding the endothelium of the human circulatory system. Thanks to this function of platelets, blood vessels receive vital microelements that help normalize the flow of red cells and the general functioning of internal organs. The degree of protection of the body (immunity) largely depends on this property.
Blood elements are also actively involved in regeneration, that is, in the healing of tissue after damage. This effect achieved accelerated process division and release from blood vessels. In other words, platelets perform the function of clogging the entire damaged area. Moreover, they promote accelerated growth of affected cells. This process refers to the division of polypeptide molecules.  During platelet activation, fibroblast growth also occurs. Also at this moment, microcomponents are produced that are responsible for cell transformation and restoration of insulin levels.
During platelet activation, fibroblast growth also occurs. Also at this moment, microcomponents are produced that are responsible for cell transformation and restoration of insulin levels.
Normal indicators
In humans, platelets should always be within generally accepted limits. IN general analysis values are given per 1 liter of blood. The specification of the entry looks like this: x10 9 /l. The normal platelet count for an adult is between 200 and 400 units. In adolescents from 15 to 18 years old, these indicators are 180-420. In children under 15 years of age, the level of corpuscles varies from 150 to 450 units. In newborns minimum threshold is 100, and the maximum is 400.
It is worth noting that in female representatives the platelet limits may be slightly lower than the above norms. This depends on physiological characteristics and hormone levels. In addition, at the time of menstruation, the minimum platelet threshold drops sharply due to blood loss. A similar situation is observed in pregnant women, when the level of regenerating cells can decrease significantly. This is due to an increase in the volume of fluid in the blood. Therefore, during the analysis, a decrease in the amount of all microcomponents is observed.  It is important to understand that platelet numbers are not the main thing. In any case, you should consult a doctor with the results of the analysis to carry out additional research to determine the effectiveness of their action. This procedure is called a coagulogram.
It is important to understand that platelet numbers are not the main thing. In any case, you should consult a doctor with the results of the analysis to carry out additional research to determine the effectiveness of their action. This procedure is called a coagulogram.
Deviations and their reasons
If a blood test shows that there is a lack or excess of platelets in the body, it is necessary to urgently undergo additional medical examination. This is the first warning sign that signals the development of a serious disease.
Since platelets are irreplaceable and vital for blood, any deviation from the norm affects the general condition of the body. A decrease in the number of corpuscles increases the risk of prolonged healing even with minimal damage. In other words, it is reduced to a minimum. As the level increases, the protective functions of platelets are activated. In this case, large connections will form in the vessels, disrupting blood flow. As a result, there is a risk of developing blood clots. Sharp deviations from medical norms may indicate the initial stage of cancer.
To prevent and maintain platelet levels, doctors recommend proper nutrition. The diet should always have plenty of vitamin B12 and folic acid.
Decreased platelet functionality
This condition occurs during a significant decrease in the number of regenerating cells in the blood. As a result of this decline, internal organs become vulnerable to infections. This has a detrimental effect primarily on the liver and thyroid gland.  The reasons for the decrease in the number of platelets and their functionality can be diseases such as rubella, leukemia, measles. The most terrible of them is cancer tumor. In addition, a decrease in levels is observed in patients after chemotherapy, as well as in cases of aspirin overdose and dehydration. Some strong antibiotics can have a detrimental effect on the growth of blood cells.
The reasons for the decrease in the number of platelets and their functionality can be diseases such as rubella, leukemia, measles. The most terrible of them is cancer tumor. In addition, a decrease in levels is observed in patients after chemotherapy, as well as in cases of aspirin overdose and dehydration. Some strong antibiotics can have a detrimental effect on the growth of blood cells.
A decrease in platelet levels requires mandatory treatment. First of all, the doctor must prescribe pharmacological drugs. And in second place are diet and herbal prevention. Traditional methods are powerless here, and delaying treatment can lead to inevitable consequences. It is important during prophylaxis not to take, for example, analgesics, Aspirin, or sulfonamide group.
Excess platelets
An increase in the level of regenerating cells indicates an oncological disease. In addition, it affects the supporting functions of platelets. An excess of corpuscles is also possible during sepsis or after surgery to remove the spleen. A separate case may be severe internal bleeding.  As a result, embolisms rapidly form in the vessels. This problem requires an immediate solution. It is worth noting that self-medication will not give any results. Only pharmacological therapy will help here. The most common drugs include Pyrabutol and Aspirin. It is also important to exclude any overload of the body.
As a result, embolisms rapidly form in the vessels. This problem requires an immediate solution. It is worth noting that self-medication will not give any results. Only pharmacological therapy will help here. The most common drugs include Pyrabutol and Aspirin. It is also important to exclude any overload of the body.
Probable diseases
With a decrease in platelet levels, there is a high risk of developing aplastic anemia, and Gaucher, cytopenic purpura.
With an increase in the number of red plates in the blood, the likelihood of hemolytic syndrome arises. But first of all, you should be checked for cancer.
Impaired platelet function of aggregation and adhesion leads to Bernard-Soulier, von Willebrand, Pudlak, and Scott syndromes.
When red cell metabolism fails, atherosclerosis, cerebrovascular and arterial diseases, malaria, asthma, and cancer are observed.
Platelets play an important role in circulatory system person. They promote blood thickening when the walls of vascular tissue are damaged, form a blood clot at the wound site and help transport useful substances. The lifespan of platelets is usually considered from the moment they are separated from the red bone marrow cell.
Habitat
Platelets begin to originate in the megakaryocyte, which is the name given to the large cell of the bone marrow. The diameter of the progenitor is 60-120 microns. When mature, it has a large cytoplasm, purple-pink grains and a rough nucleus of indeterminate shape.
At this stage, small scales peel off from its cytoplasm. Their third part is localized in the spleen, while the remaining bodies are released into the general bloodstream. Retention in the spleen is due to slow progression through uneven cords. Therefore, when this organ is diseased, the overall level in the blood decreases.
Type of platelet
When taking an analysis, only mature cells are assessed; their number in the body of a healthy person is about 90%. But there are other types of plates:

- Young ones are larger in size than mature ones. If their excess is recorded, this indicates that the bone marrow is working hard, especially with significant blood loss.
- Old ones are distinguished by the presence of a thin rim along the edge of the cell and an increased number of granules. Their appearance indicates the development of a malignant tumor.
- Forms of irritation can be recognized by large size and non-standard plate shape. Their origin is associated with impaired release of platelets in blood diseases.
Platelet structure
Mature plates have a disc-shaped shape with clearly defined boundaries, their size on average reaches 2-5 microns. They do not contain a nucleus, but have a granulomer consisting of azurophilic grains in a small amount from 5 to 20 pieces per unit.
If you make a cut, you can see three zones of the cell structure:
- Peripheral. In its structure there is a supramembrane region, which is responsible for platelet activation. The membrane itself is needed to ensure a timely and correct blood clotting reaction.
- The organelle department contains 4 types of granules. The main function of which is to accumulate factors responsible for blood clotting. This ability remains active for a long time, despite the low lifespan of platelets in humans.
- Sol-gel zone. The main component of this area is mitochondria. Due to redox reactions, energy is released in them, which nourishes the cell, giving it the ability to move.
Life cycle and functionality
After final separation from the megakaryocyte, the lifespan of platelets averages 7-11 days. But their activity and functionality gradually decreases. Largest accumulation, and subsequently destruction occurs in the liver and spleen.
Platelets differ in their functionality and unique properties. With the help of receptors, they can stick to the site of damage, this process is called adhesion.
When the plates come into contact with endothelial collagen, ions enter the cytoplasm due to the opening of calcium channels. As a result, the activation system is launched and the cells change their shape and size.
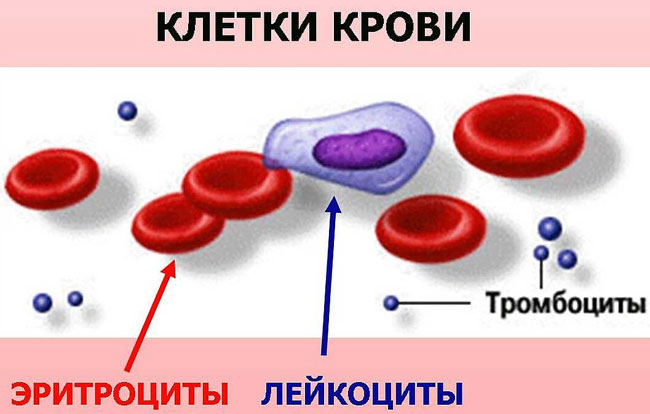
Normal platelet count in human blood
The average duration of maturation of one megakaryocyte is 5 days, after which it releases about 3000 platelets. In an adult, the norm of plates in a blood test is slightly higher than in a child, and is 150-350 x 10 9 / l; in children, an indicator of 150-250 × 10 9 / l is considered good.
These values are relative and may vary depending on gender, age and the presence of diseases. If the number of cells increases or decreases significantly, then this is a signal of the onset of a disease.
What does a change in platelet count indicate?
Thrombocytopenia
A finger prick blood test can determine the overall picture of the disease. A decrease in platelets indicates thrombocytopenia. It occurs due to:

- Blood diseases such as leukemia, anemia.
- The presence of infectious diseases.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the bone marrow or kidneys.
Also, their decrease in the blood can be observed in women during hormonal changes in the body, for example, during menstruation or pregnancy.
Some medications or alcohol can have the same effect.
With thrombocytopenia, internal bleeding can occur at any time, as the vessels become fragile, losing their elasticity. You should be examined at the first signs of illness, such as:
- Constant appearance of blood when brushing teeth.
- The appearance of bruises with a slight injury.
- Prolonged stopping of bleeding with a shallow cut.
- Regular nosebleeds.
- Heavy and prolonged menstruation.
Thrombocytosis
An increase in platelet count indicates an increase in their production, which can lead to the formation of blood clots. This is due to:
- Inflammatory diseases of internal organs.
- Tuberculosis, cirrhosis.
- Presence of cancer.
- Previous bleeding, sometimes due to surgery.
- Medicines from a number of corticosteroids.
- Diseases of the circulatory system.
- Operations to remove the spleen.
Platelets play an important role in ensuring a full human life. That is why it is important to know how long they last and how to protect yourself from a decrease or increase in this indicator in the blood.

