Signs of appendicitis are varied and expressed to a greater or lesser extent depending on the anatomical changes in the appendix, its location, the time elapsed from the onset of the disease, age and a number of other conditions. Appendix- a vermiform appendage of the cecum, which is located almost on the border between the small and large intestines. One of them puts life at risk; Thus, one to appendicitis is fast and without any delay. Classic appendicitis responds quickly to appendectomy, although it sometimes resolves spontaneously. It remains to be debated whether there is benefit to elective appendectomy in these patients to prevent a recurrent episode. Atypical appendicitis, that is, associated with a purulent or purulent application, is more difficult to diagnose and most often causes complications, even if surgery occurs quickly. Mortality and severe complications, although uncommon, do occur, especially if they are accompanied, if they persist, or if the disease resolves without treatment. One unusual complication of appendectomy occurs when inflamed residual tissue remains after an incomplete appendectomy. Many rodents, some predators, monkeys and, of course, humans have a vermiform appendix. The length of the human appendix is on average 5 - 15 cm, diameter - about 1 cm. Presumably, its main task is to protect small intestine from bacteria inhabiting the cecum. Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix. This disease is extremely common and requires emergency surgery. In the overwhelming majority of cases, signs of acute appendicitis such as pain, dyspeptic symptoms, dysuric disorders, and intestinal dysfunction are noted. Special groups, such as scouts, divers, astronauts and others who do not have easy access to a surgeon, undergo prophylactic appendectomy. If an appendectomy is imminent and other pathology is detected and the appendix is healthy, a random appendectomy will be performed. Appendicitis is a condition in which the appendix becomes inflamed. Your symptoms can become very uncomfortable, painful and potentially fatal if left untreated. Sudden appendicitis is the most common cause acute pain in the abdomen requiring surgery in the United States. Additionally, more than 5% of the population develops appendicitis at some point. Appendicitis can happen to anyone, regardless of age. In traditional medicine, it is customary to consider the symptoms of appendicitis in the following sequence: In medical practice, acute and chronic appendicitis are distinguished. Classification of morphological forms acute variety as follows: This will prevent it from getting worse and causing more complications. Stomach pain is often the first symptom of appendicitis. The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases describes the pain as "a different type of pain than you've ever felt before." The pain may be sudden and come without notice. As it worsens, the pain will likely move to the lower right side of the abdomen. The feeling may become more intense over the next few hours and is worse with movement, deep breathing, coughing or sneezing. Symptoms of classic appendicitis appear in only 50% of people who develop the disease. This classification corresponds to the phases of development of the disease, up to the destruction and death of appendix tissue. Most often, the attack lasts from 2 to 4 days. Some patients may experience classic symptoms such as pain or stomach pain. Others may have less common symptoms of appendicitis. Children and infants may not experience pain in a specific area. The sensation may spread throughout the body or be absent altogether. Additionally, children and infants may have less frequent bowel movements, if at all. Diarrhea may be a symptom of another disease. Children and infants may not experience pain in the same way as older patients. However, research shows that stomach pain is still the most common symptom of appendicitis for them. In medical surgical practice, clinical signs of appendicitis are distinguished: At the first signs of appendicitis, you should immediately consult a doctor to exclude dangerous and life-threatening sick consequences. Older adults and pregnant women may also experience various symptoms of appendicitis. Stomach pain may not be as severe or specific for these patients. For pregnant women, stomach pain may move upward to the upper right quadrant after the first trimester. They may also have some back discomfort or side pain. In both groups, people should look for less common symptoms of appendicitis. These include nausea, vomiting and fever. Stomach pain can often be caused by another condition. Stomach pain can be a symptom of other conditions that may seem abnormal, like appendicitis. The following conditions also commonly cause stomach pain, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Stomach injuries Constipation Inflammatory bowel diseases, including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis Stools, parasites or tumors that obstruct the internal part of the appendix Damage or damage to the abdomen. Appendicitis is a life-threatening condition and requires immediate attention medical care. The condition will likely get worse and it will remain untreated longer. Medical experts recommend going to the emergency room as soon as symptoms begin so that a doctor can diagnose and treat appendicitis. The appendix is an organ of the human body in the form of a tissue tube closed at one end. It is located in the cecum, the area where the large intestine or large intestine begins. It usually measures about 4 inches in length and is located on the right side, on the lower side of the abdomen. The tongue at the beginning of the disease is moist, often covered with a white coating. Free lies on the back or right side; changes in body position, coughing, laughing, sneezing sharply increase abdominal pain. When examining the abdomen, there may be a lag in the right lower quadrant of the abdominal wall during breathing. On palpation, muscle tension and sharp pain in the right iliac region are detected. Positive symptoms of peritoneal irritation (Shchetkin-Blumberg, Razdolsky, Voskresensky symptom) can also be detected here. There are no pathognomonic symptoms of acute appendicitis; all symptoms are caused by the phenomena of local peritonitis. Pain, as a rule, intensifies when the patient is positioned on the left side (Sitkovsky's symptom), especially during palpation (Barthomier-Mikhelson's symptom). With a retrocecal location of the process, there may be a positive Obraztsov’s sign—increased pain when raising the straightened right leg. This symptom should be checked very carefully, since with rough pressure on the abdominal wall, perforation of the appendix is possible. The temperature is often elevated to low-grade levels. In the blood - leukocytosis with a shift of the formula to the left. During a digital examination of the rectum or vaginal examination, pain is noted on palpation of the right wall of the pelvis (especially when the process is in the pelvic position). The presence of red blood cells and white blood cells in the urine does not exclude acute appendicitis. The appendix is known to be an organ that does not work, unnecessary for survival. However, a study published in the Journal of Theoretical Biology suggests it may serve a purpose. Researchers from Medical center Duke University in Durham, North Carolina, believes the supplement may play a role in maintaining a healthy immune system. They say the app helps create good microbes to help our bodies protect other good microbes and fight bad guys. Typically, a healthcare provider will diagnose appendicitis using the following procedure. The diagnosis of acute appendicitis in typical cases is simple, but the atypical location and peculiarities of the course of the inflammatory process sometimes make diagnosing the disease extremely difficult. Differential diagnosis is carried out with pyelitis, renal colic (see Urolithiasis), acute adnexitis, ectopic pregnancy, acute enteritis, mesadenitis, diverticulitis, acute cholecystitis, acute pancreatitis, perforated gastric and duodenal ulcers, right-sided pneumonia, herpes zoster, etc. acute simple and destructive appendicitis. In the latter case, the symptoms of acute appendicitis are more pronounced: pain is stronger, symptoms of peritoneal irritation are more clear, leukocytosis and temperature are higher. However, complete correspondence of the clinical picture of the disease with the nature of the detected morphological changes in the appendix is still not observed. You will be asked to provide detailed information about what symptoms you are experiencing, the severity, and for how long. To exclude others possible problems health, the doctor will want to know details about the patient's medical history. Any other medical condition or surgery that the patient has had or has had in the past. If the patient drinks alcohol or takes any recreational drugs. If the patient is taking any medications or supplements. . The doctor will perform a physical examination to get more information about the patient's stomach pain and be able to pinpoint appendicitis. The course of acute appendicitis in children, the elderly and pregnant women has its own characteristics. In children, underdevelopment of the greater omentum and the body's hyperergic reaction lead to rapid progression of the inflammatory process and the development of peritonitis. Diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children in the initial stage of the disease is difficult: nausea, repeated vomiting, high fever, diffuse abdominal pain, and therefore diagnostic errors are often made. In older people, a decrease in the body's reactivity causes the clinical symptoms of the disease to fade, which can be a reason for delayed diagnosis and hospitalization. Hence the prevalence of destructive forms of acute appendicitis and often appendiceal infiltrates. In pregnant women, displacement of the dome of the cecum and the appendix by the uterus leads to a change in the typical localization of pain, and the location of the appendix behind the uterus leads to a decrease in the severity of peritoneal symptoms. You will apply pressure or touch certain areas of the abdomen. Pelvic and rectal exams may also be used. Your doctor may order laboratory tests to confirm a diagnosis of appendicitis or look for signs of other health problems. Blood and urine tests are required. Doctors may also order blood and urine samples to test for pregnancy. If they feel it is necessary to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor may also order imaging. Tests may include an abdominal ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, or computed tomography. These tests can reveal the following sources of stomach pain. Treatment for appendicitis usually begins with antibiotics and venous fluids. Some mild cases of appendicitis can be completely treated with fluids and antibiotics. The next most common step for treating appendicitis is surgery. The procedure is called an appendectomy. Removing the app reduces the risk of rupture. Treating early appendicitis is also important to reduce the risk of complications that can lead to death. There are two types of operations associated with appendectomy. Surgeons make several small incisions and use special instruments to remove the appendix through them. Laparoscopic surgery may result in fewer complications such as hospital-associated infections. Recovery time is usually shorter. patients limit their physical exercise during the first 3-5 days after surgery. The surgeon is allowed to clean the inside of the abdomen to prevent infection. Sign #2 This is by far one of the most common reasons for emergency surgery performed in hospitals around the world. Although it does not usually return gravity, it is one of the conditions that concerns many people the most, especially the life-long consequences that may lie in the fact that it is left undiagnosed and untreated over time. The reason that leads to the concern of both doctors and especially patients is that it does not always show obvious symptoms or signs, so that sometimes it is confused with other changes that delay the diagnosis, which in fact should be made quickly possible . Sign #3 Moreover, the problem that medically causes appendicitis is not inflammation of the appendix itself, but that the condition develops to such an extent that it causes peritonitis, which poses a great risk to the life of the appendicitis. A person who suffers. That is, when the application ends up necrotic and tends to rot inside the abdominal cavity and can even affect the rest of the organs digestive system. As its name suggests, appendicitis mainly consists of inflammation of the appendix. The appendix is located at the beginning of the colon, especially in the lower right abdomen. It has a characteristic shape that resembles the appearance of a worm, and its color is usually pink when not flammable. Treatment of appendicitis is only surgical in a hospital! Due to the threat of development of peritonitis and sepsis, then death. The operation is indicated not only in every clear case from a diagnostic point of view, but also in reasonable suspicion for acute appendicitis, if it is impossible to exclude acute inflammation of the appendix based on clinical signs and special research methods (including laparoscopy). If signs of peritonitis are pronounced, it is advisable to administer antibiotics (aminoglycosides) and metronidazole before surgery. In thin, young patients, appendectomy is usually performed under local anesthesia with a 0.25-0.5% novocaine solution. In case of severe pain syndrome in patients with unstable psyche, children, pregnant women, elderly and senile patients, preference should be given to general anesthesia. Patients with acute appendicitis without signs of peritonitis undergo surgical treatment as planned. Its main function is to protect the abdominal organs from any type of infection, and on the other hand, to allow it to slip through the abdominal cavity. Therefore, peritonitis consists of inflammation of the peritoneum. This can be caused not only by inflammation of the appendix and subsequent infection, but also by trauma, other infections, or the presence of chemical irritants. This is the most common, common and obvious. This is usually a type of severe pain that begins suddenly. The location where this pain occurs depends directly on the cause of the inflammation, so that as the infection progresses, the pain usually affects the entire abdomen, becoming generalized.
The main and constant sign of appendicitis is pain, which is of a varied nature.
Symptoms of appendicitis include patient complaints, history of the disease (how it developed) and some other signs. The main symptoms and signs of acute appendicitis are: abdominal pain (first in the lower abdomen and then in the right side), fever, nausea, vomiting. If you notice the first signs of appendicitis, you should immediately consult a doctor or even call an ambulance. Types and forms of appendicitis
Symptoms of appendicitis
Where is appendicitis located?
Symptoms in children and infants
Symptoms in older and pregnant women
Other conditions with similar symptoms
 Clinical manifestations of acute appendicitis depend on the nature of the morphological changes in the appendix, its location, the age of the patients, and the nature of the associated complications. The initial symptom of the disease is a sudden dull pain without clear localization in the upper abdomen or navel area. After A-6 hours (with fluctuations from 1 to 12 hours), the pain moves to the right iliac region. A change in the localization of pain with the appearance of soreness in the right iliac region indicates the alarming appearance of somatic pain caused by irritation of the visceral peritoneum (i.e., inflammation has captured all layers of the wall of the appendix). The localization of pain depends on the location of the appendix: in a typical position, the patient feels pain in the right iliac region, in a high position - almost in the right hypochondrium, in a retrocecal position - on the lateral surface of the abdomen or in the lumbar region, in a pelvic position - above the pubis. Nausea is a common symptom of acute appendicitis; sometimes, especially at the beginning of the disease, vomiting is possible. In most cases, the stool is not disturbed. When the appendage is located near the cecum or rectum or among loops of the small intestine, inflammation can spread to the intestinal wall, leading to fluid accumulation in the intestinal lumen and diarrhea.
Clinical manifestations of acute appendicitis depend on the nature of the morphological changes in the appendix, its location, the age of the patients, and the nature of the associated complications. The initial symptom of the disease is a sudden dull pain without clear localization in the upper abdomen or navel area. After A-6 hours (with fluctuations from 1 to 12 hours), the pain moves to the right iliac region. A change in the localization of pain with the appearance of soreness in the right iliac region indicates the alarming appearance of somatic pain caused by irritation of the visceral peritoneum (i.e., inflammation has captured all layers of the wall of the appendix). The localization of pain depends on the location of the appendix: in a typical position, the patient feels pain in the right iliac region, in a high position - almost in the right hypochondrium, in a retrocecal position - on the lateral surface of the abdomen or in the lumbar region, in a pelvic position - above the pubis. Nausea is a common symptom of acute appendicitis; sometimes, especially at the beginning of the disease, vomiting is possible. In most cases, the stool is not disturbed. When the appendage is located near the cecum or rectum or among loops of the small intestine, inflammation can spread to the intestinal wall, leading to fluid accumulation in the intestinal lumen and diarrhea.Analysis of the patient's medical history
Order laboratory tests
 Sign #1
Sign #1
Abdominal pain– one of the first and main symptoms of acute appendicitis. Most often, pain with appendicitis is not localized, and the patient cannot pinpoint exactly where it hurts. After some time, the pain moves to the right lower abdomen - this symptom most often indicates appendicitis; you will not find it in any other disease. Once it occurs, the pain may intensify or decrease, but it never completely goes away. Abdominal pain may worsen when walking, coughing or sneezing, laughing, or changing body position. Characteristic feature Appendicitis can cause pain in the legs, most often in the right.
Slowly press your hand into the lower right abdomen and release quickly. If the patient feels sharp pain precisely when quick removal hands, this can only mean one thing - call an ambulance quickly, it’s appendicitis. This test is called the Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom.Risk factors complicating appendicitis
Delayed treatment can significantly increase the risk of complications with appendicitis.
Fever is also one of the symptoms of appendicitis. The temperature in this disease is not high, usually 37-38°C, but the presence of temperature helps to distinguish appendicitis from other diseases with similar symptoms. There may be no temperature with appendicitis, but this does not mean that there is no appendicitis. Be careful and watch out for other signs.
Nausea, vomiting, general weakness, loss of appetite. The feeling of pain in the first hours is often accompanied by reactions gastrointestinal tract For example, stomach upset may occur in children and adults. Vomiting is often one-time, and if it is repeated, this may indicate serious complications and a threat to life for the patient. Children may vomit repeatedly. Treatment of appendicitis
What are the symptoms and signs of peritonitis?
Greetings, dear readers of Alexey Shevchenko’s blog “ Healthy image life." Today, one of my friends shared good news with me: her ten-year-old daughter was discharged from the hospital, where she underwent surgery to remove her appendix. Fortunately, everything turned out well, and now everyone remembers the excitement they experienced as nightmare. The doctor said that the girl was taken to the hospital just in time - a few more hours of delay, and a rupture of the appendix would have been inevitable, and it would have been long and difficult to treat such a life-threatening condition.
The cause of the illness was, generally speaking, trivial: the child accidentally swallowed fish bones during a picnic, and the lumen of the appendix became blocked. First dangerous symptoms The developing disease appeared quite early, but the parents decided that it was ordinary diarrhea, which often occurs in children in the summer. Such carelessness almost turned into a tragedy.
Impressed by all this news, I decided to devote today's article to the topic of signs of appendicitis.

Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendage of the cecum (appendix). This appendage is very small in size, but can cause very big trouble if inflammation begins in it. (You can read about the causes of appendicitis).
You can get appendicitis at any age. The incidence rate is so high that almost 10% of the population loses this organ as a result of surgery.
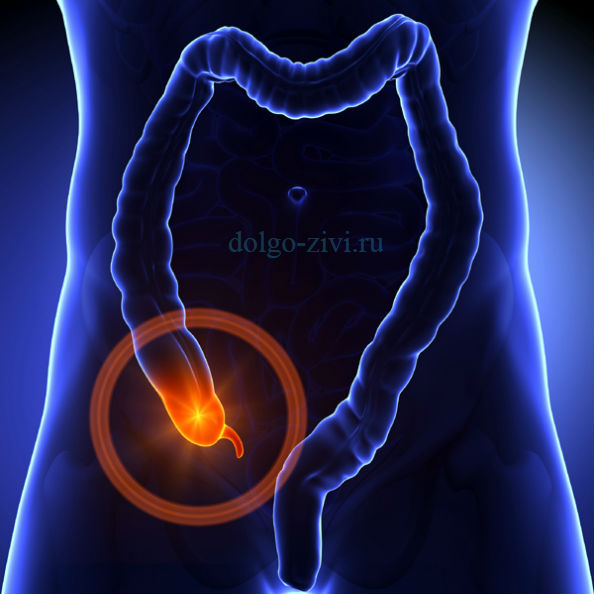
Statistics show that in rich countries this disease is much more common than in poor ones. Some experts explain this imbalance by the peculiarities of the diet (in developed countries, food contains little fiber and is overloaded), and others by the fact that in third world countries, diagnostics and recording of morbidity are far from perfect.
Main symptoms of appendicitis
The signs of acute appendicitis (or, as people say, “signs of inflammation of appendicitis”) are quite characteristic, but it is difficult even for specialists to understand them.

Acute inflammation of the appendix is almost always accompanied by:
- pain in right side belly;
- nausea and vomiting;
- lack of appetite;
- slight temperature.
But all this happens with trivial poisoning, and with a cold, and with a hundred or two other various diseases. How to distinguish one from the other? How to recognize the disease? How to check, how to understand that you have appendicitis? The easiest way is to see a doctor - he will conduct necessary tests and accurately diagnose. But since appendicitis occurs very often, it is useful for everyone to know the subtleties of its symptoms. So, let's look at how appendicitis manifests itself in a little more detail.

Abdominal pain . The pain can vary in intensity. Sometimes it is very acute - then it is easier to diagnose; but it also happens that the pain is dull and so poorly localized that a person cannot even accurately point to the place where it hurts (this is typical for older people).
In most cases of appendicitis, the pain quickly moves to the right side of the abdomen. It may wax and wane, but it does not subside completely.
The pain noticeably intensifies when walking or coughing. Sometimes it can radiate to the right leg.
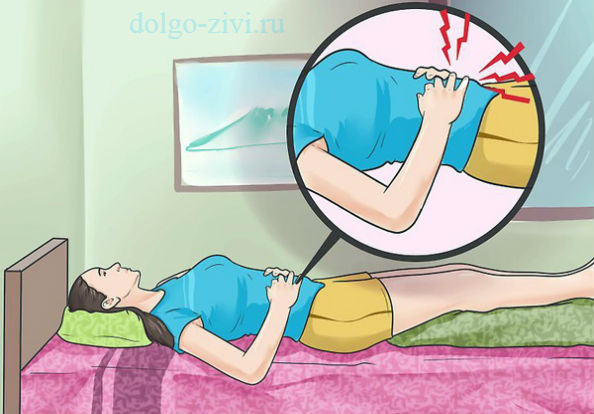
A very informative test for appendicitis is the Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom. To check for its presence, you need to gently but intensely press your hand on the right lower abdomen, and then suddenly release your hand. If at the same time the patient feels an explosion of pain, then the probability of appendicitis is very high, and an urgent need to go to the hospital.
If the pain sharply intensifies when trying to lift the straightened right leg from a supine position, then we can almost certainly say that the person has appendicitis.
Often the pain subsides a little if you lie on your left side and curl into the fetal position.
Vomiting and nausea. The first episode of vomiting with appendicitis often begins even before pain occurs. Vomiting can be one-time or repeated. It may also be accompanied by an upset stomach. During defecation there may be dull or sharp pains in the rectum, back and lower abdomen. Urination can also be painful.
Sometimes, instead of diarrhea, patients develop severe diarrhea.
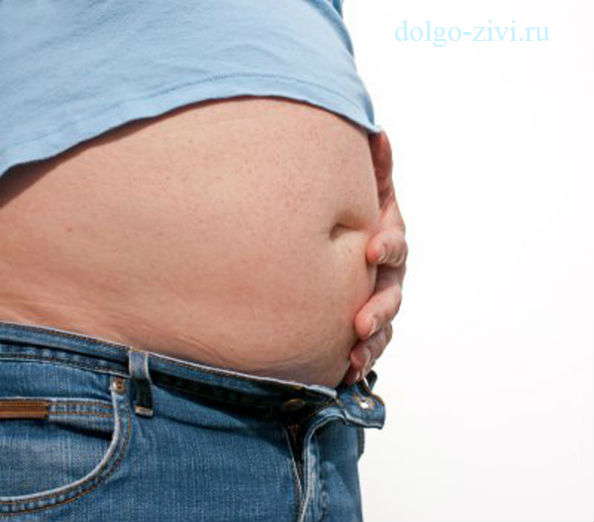

Hard belly. This symptom is quite typical for inflammation of the appendix. If, while feeling your stomach, the patient notices that it has become much harder than usual, and this is accompanied by pain, nausea, or, then this is a very good reason to seek medical help as quickly as possible.
Fever. With ordinary appendicitis, the temperature does not rise much. More often it is always in the range from 37 to 38 degrees. In this case, the condition is accompanied by chills, trembling and sticky sweat throughout the body. But if the temperature rises higher, this is already a serious signal and requires immediate medical attention.
Features of appendicitis in children
In childhood, the risk of developing appendicitis is much higher than in adulthood or old age. The greatest danger lies in children aged 10-12 years. At this age, lymphatic follicles develop intensively, and the appendix becomes especially vulnerable to inflammation.
In addition, children are much more likely than adults to swallow small objects and are more susceptible to infection with worms, which also creates a favorable environment for the development of appendicitis. For example, in the first half of the last century, more than 40% of cases of appendicitis in children were due to the fact that roundworms blocked the lumen of the appendix.
Today appendicitis is one of the main reasons for surgical operations abdominal cavity in children. At the same time, for some reason, boys get sick more often than girls.
![]()
The set of symptoms of appendicitis in children is almost the same as in adults, but the disease develops much faster. Therefore, almost 30% of cases of childhood appendicitis occur with a ruptured appendix.
A huge difficulty for parents and doctors is the fact that children younger age either they don’t speak at all, or they can’t really explain where it hurts. That's why Special attention you should pay attention to the following symptoms:
- cardiopalmus;
- frequent urination; the child experiences increased pain;
- elevated temperature;
- lack of appetite;
- vomit;
- increased pain when moving – the child is lethargic and tries to move as little as possible.
If parents think that their child has appendicitis, they need to see a doctor without hesitating for a minute. If this is true, the condition can deteriorate rapidly, and within just a few hours the inflammation can become extensive.
Features of symptoms during pregnancy
Appendicitis in pregnant women is also not uncommon. About one in a thousand expectant mothers have to deal with this problem. Most often, this disease develops during the first two trimesters.
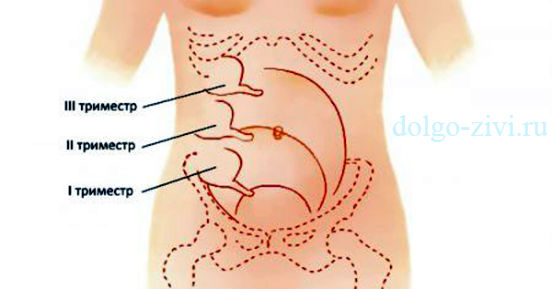
If a woman carefully monitors her condition, then it will not be difficult for her to notice that something is wrong. So, nausea, vomiting, problems with appetite are inevitable companions of pregnancy. But when the body is healthy, they go, so to speak, according to a certain schedule.
If appendicitis begins, then vomiting does not occur at the usual time, nausea becomes much stronger, appetite disappears completely, and all this is accompanied by strong pain in the navel area, which gradually shifts to the right side. If you lie on your right side, the pain intensifies significantly. Waves of pain are accompanied by vomiting.
The most striking symptoms will be fever, unusual sweating, and severe pallor.
Why is it difficult even for doctors to diagnose appendicitis?
Despite enough a large number of characteristic symptoms, diagnosing appendicitis often causes difficulties even in experienced doctors. The fact is that the first signs of the disease are varied, and the body structure of each person is absolutely individual, and there is no clear answer to the seemingly simple question “on which side is a person’s appendix?” simply doesn't exist. In most cases, the appendix is located in the lower right side of the abdomen, but quite often it is located higher, and sometimes it can be in the liver area. There are also cases where the appendix is located on the left side.
Like all other organs of the digestive system, the appendix is attached to the wall of the abdomen with the help of a special organ - the mesentery. In some people, the features of the mesentery are such that they allow the appendix to become dislodged.
In addition, the size of the appendix itself is different people can vary greatly: its thickness varies from 0.5 to 1 cm, and its length from 0.5 to 23 cm.
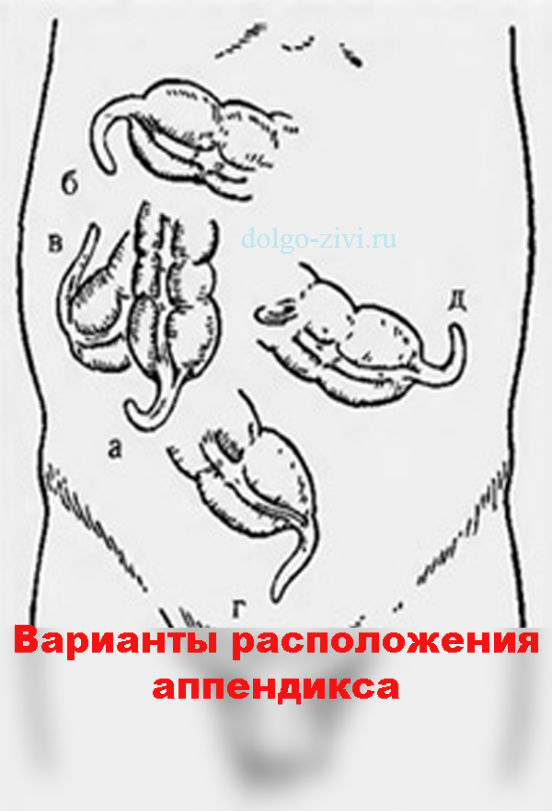
Additional complications are created by the fact that the appendix can be located near completely different organs: behind the colon, among the pelvic organs (this is typical for women), near the gallbladder. Therefore, inflammation of the appendix (appendicitis) may look like inflammation of completely different organs.
The picture becomes even more confusing when we consider the fact that many other diseases can mimic a full-blown attack of appendicitis, although the appendix itself is completely healthy. This is due to the same tightness in the abdominal cavity. The organs are located literally close to each other, and the symptoms are confused.
More often than others, an attack of appendicitis is imitated by the following diseases.
- Meckel's diverticulitis. A small protrusion of the ileum (called a Meckel's diverticulum) is a congenital abnormality that occurs in approximately 2% of newborns (boys are twice as likely to suffer from it as girls).
- Inflammation of the pelvic organs (rectum, bladder, a number of gonads). Quite often, gynecological diseases such as inflammation and fallopian tube give a picture characteristic of appendicitis.
- Inflammatory diseases of the organs of the right upper abdomen. The pain often radiates downwards, and even to an experienced specialist it may seem that a person has appendicitis. More often than others, such “deceivers” are perforated duodenal ulcer, cholecystitis, and liver abscess.
- Diseases of the right kidney. This organ is a close neighbor of the appendix, so the manifestations of nephritis are very easy to confuse with appendicitis.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
If the appendix is removed, is appendicitis no longer a threat?
It sounds paradoxical, but removal of the appendix does not guarantee complete absence problems in the future. They are rare, but they do occur.
Obviously, it is absolutely impossible to remove the appendix without the slightest residue. After amputation of the appendage, the so-called stump of the appendix remains. Under unfavorable circumstances, it can become inflamed in the future and also cause other complications. Therefore, for those who have already experienced surgery once, the repeated principle of “appendicitis” is not at all excluded.
Inflammation of the stump of the appendix is much more common in those patients whose operation was difficult - appendicitis was in an advanced form; the inflammation has managed to spread to neighboring tissues; there was a ruptured appendix.
The symptoms of inflammation of the stump are completely similar to the symptoms of appendicitis, so even after amputation you should not immediately throw them out of your head.
And now I suggest watching a short video in which the doctor briefly lists the most basic symptoms of appendicitis that everyone should know.
I hope, dear readers, you have found something for yourself useful information In this article. If yes, share links to the article with your friends on in social networks. Also, I would be very interested to know your opinion, which you can express in the comments.
You may also be interested

