Antibiotic sensitivity tests is a laboratory research method that allows you to select an effective antibiotic therapy regimen. Antibacterial therapy is used in the treatment of diseases caused by an infectious agent. Pathogens have different structures and morphological qualities, and therefore some antibiotics may be ineffective. To prevent the prescription of ineffective treatment, antibiotic sensitivity tests have been developed.
Sensitivity to antibiotics in pathogens of the same disease periodically changes. This is due to the fact that microorganisms adapt to negative impact drugs, changing the structure of its cell wall.
Why is antibiotic sensitivity testing necessary?
There are several reasons why doctors prescribe antibiotic sensitivity tests to patients:
- identifying the most effective antibiotic for a given clinical case
- replacing an antibacterial drug if it is ineffective
- replacement of the drug to prevent addiction to the drugs of this pharmacological group
- replacing the drug due to the development of allergic or other adverse reactions.
Determining sensitivity to antibiotics is an absolutely safe procedure for the patient, since it only requires a venous blood sample. The main part of the study is carried out in the laboratory without direct contact with the patient.
What methods exist for determining sensitivity to antibiotics?
 Antibiotic disc method. The cups are abundantly seeded with pathogenic microorganisms, after which a disk impregnated with a certain type of antibacterial drug is placed on its surface.
Antibiotic disc method. The cups are abundantly seeded with pathogenic microorganisms, after which a disk impregnated with a certain type of antibacterial drug is placed on its surface.
The effectiveness of the antibiotic is assessed by inhibiting the growth of microorganisms in the dish. In the absence of sensitivity, the microorganism will continue its unhindered growth on the nutrient medium.
E-test. Test strips impregnated with antibiotics are used. The strip is placed on a nutrient medium with colonies of the pathogen. The effectiveness of the antibacterial drug is judged by growth retardation.
The serial dilution method allows not only to determine sensitivity to antibiotics, but also to calculate the dose of the drug required for a bacteriostatic effect.
What is the material for isolating the causative agent of the disease?
The material for testing sensitivity to antibiotics is selected depending on the location of the pathological process. Select a biological fluid in which the concentration of the pathogen will be maximum and will give good growth on a nutrient medium. The following materials can be taken as materials:
- saliva
- urine – especially with urinary tract infections and pyelonephritis
- scraping - for skin rash with serous or purulent discharge
- prostate secretion – for infections that are predominantly sexually transmitted
- swab from the walls of the throat - for sore throats
- nasal rinses – for acute respiratory diseases
- blood
Antibiotic sensitivity tests in a private clinic
If the doctor recommended testing the sensitivity of a microorganism to antibacterial drugs, then it is worth doing this relatively inexpensive examination. In order to get everything done quickly and efficiently, it is better to contact a private laboratory, where your analysis will be accurate.
Extremely important have deadlines that may be significantly delayed in a clinic. Replacement of an ineffective antibiotic should be carried out in the first 5 days from the start of treatment.
The staff at the “Your Doctor” help desk will tell you the addresses of private clinics that have laboratory diagnostic capabilities to test microorganisms for sensitivity to antibiotics.
A smear for antibiotic sensitivity is an integral part of a microbiological study. In this case, absolutely different material, starting with mucous discharge from a woman’s vagina or the contents of a man’s urethra and ending with phlegm and mucus from. The material depends on the type of disease, its shape and severity.
Why is this necessary?
Antibacterial therapy is by far the most widely used method of treating many diseases. This is due to the high efficiency and relative harmlessness of the use of antibacterial agents. But there is a problem that does not always allow you to achieve the desired result - some pathogenic microorganisms are resistant to certain drugs, so you need to carefully select the appropriate remedy.
Modern pharmaceuticals provide us with a wide selection of antibacterial agents. In most cases, three or more drugs can simultaneously cope with a particular pathogen. Therefore, in order to determine the most effective drug for a given case, it is necessary to conduct a sensitivity test. This type of analysis is used not only when selecting a method of treatment for sexually transmitted diseases, but also to select therapy for other diseases of an infectious nature. Doctors recommend that antibacterial therapy for any disease begin with determining the sensitivity of pathogenic microflora to the drug.
Sensitivity testing is necessary to:
- determine the most suitable drug;
- prevent the pathogen from becoming addicted to the product used;
- replace the drug in time if there is an individual intolerance;
- reduce the duration of therapy to a minimum.
Carrying out the procedure
Diagnosis of sensitivity to antibiotics is an absolutely safe and painless test. Initially, the material is collected, after which a sensitivity analysis is carried out directly.

Depending on the type of disease and its causative agent, the biomaterial can be:
- discharge from the cervical canal;
- discharge from the urethra;
- mucous discharge from the mouth, nasal cavity or pharynx;
- prostate secretion or semen;
- breast milk, etc.
The sensitivity determination procedure itself can be carried out using several methods:
Discs with antibacterial agent. Pathogenic microorganisms are placed in a container called a Petri dish. Then a special circle (disk) is placed on the surface of the bowl, which is soaked in a variety of antibacterial drugs. The death of microorganisms under certain antibiotics is a positive result of the sensitivity test;
E-test. In an ideal environment for bacterial growth, special strips are placed on which various antibacterial agents are applied. If, when adding a separate strip, the growth of pathogenic microorganisms stops, therefore, this type of bacteria is sensitive to this drug;
Serial breeding method. This method allows you not only to determine the effectiveness of a particular product, but also to calculate the required dosage. To do this, an equal number of pathogenic microorganisms with an excellent concentration of antibiotic are introduced into an environment favorable for bacterial growth.
Preparing for diagnosis
In fact, diagnosing antibiotic sensitivity does not require specific preparation.

But at the same time, there are some rules that allow you to obtain the most reliable analysis result. Namely:
- if the necessary biomaterial is saliva, then it should be collected on an empty stomach;
- when used as a product, you need to take the first morning portion, be sure to first carry out hygiene procedures;
- if antibiotic sensitivity testing is carried out to select appropriate treatment for diseases of the genitourinary system, that is, a sample is taken from the vagina, urethra or prostate, then it is necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse two days before the procedure.
Determining sensitivity to antibacterial agents is an integral attribute of selecting an effective treatment for any disease, because this is how you can choose the most suitable effective drug in each specific case.
Therefore, a sensitivity smear will not only provide correct selection treatment regimens and the effectiveness of the therapy used, but will also eliminate the likelihood of relapse, and also shorten the duration of treatment as much as possible.
Diseases, both serious and not too serious, are, unfortunately, not uncommon. In the fight against some diseases it is impossible to do without antibiotics. Their use is assessed differently. Doctors were divided into two camps: their supporters and their opponents. If you have a need to use antibiotics, then first of all you need to find out how your body will perceive them. This can be done using antibiotic sensitivity testing. Decoding the analysis will clarify everything.
What is it?
This procedure is based on the fact that each group of microorganisms that live in our organs is sensitive to any group of antibiotics. Sensitivity manifests itself in stopping their growth and reproduction, which ultimately leads to the death of these microorganisms. Based on this analysis, a conclusion is drawn about which antibiotics will be more effective in combating specific bacteria.
What is analysis and its decoding?
Antibiotic sensitivity - what is it? Now there are three ways to determine the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics:
- diffuse;
- bacteriological analyzer;
- serial breeding.
The first is that the test drug is sprayed into a medium created by paper disks.
The second method mainly consists in the fact that, based on the bacteriological analysis performed, the sensitivity of microorganisms to the antibiotic is revealed, the result is recorded in a special table, and it is deciphered. Sensitivity to antibiotics becomes clear to the specialist.
The third method is considered the most accurate. When using it, bacteria must be serially diluted in antibiotic broth.
In general, regardless of the chosen method, the essence of the analysis comes down to the fact that the causative agent of the disease is isolated in its pure form and its reaction to a particular antibiotic is carried out, the sensitivity of the microflora to antibiotics is determined. Deciphering this analysis in these aspects is extremely important.
What is it based on?
It is extremely important to do the analysis based on sterile fluids of the organs or tissues from which the pathogen is taken. These include:
- blood;
- spinal cord fluid;
- urine;
- vaginal microflora;
- microflora of the urethra.
The result of the analysis is a list of antibiotics to which the microorganism under study was or was not sensitive. This result is provided in the form of a list called an antibiogram. As used measuring unit is used then minimum quantity medicine that is necessary to destroy the microorganism that causes the disease.
Types of microorganisms studied
Conventionally, all microorganisms can be divided into three groups. The division is based on antibiotic resistance.
We can highlight:
- sensitive pathogens;
- moderately resistant pathogens;
- resistant pathogens.
In order to cause the death of sensitive microorganisms, the usual dose of the drug is enough. For a moderately resistant microorganism, the maximum dose of antibiotic will be needed. And the maximum possible dose of antibiotic will not help to combat resistant microorganisms.
Based on the result of the analysis, when it has been deciphered, sensitivity to antibiotics has been identified, the doctor understands what dose of medicine should be prescribed to the patient. In addition, he comes to the conclusion that the most effective drug and the duration of treatment.
However, it is necessary to take into account that the sensitivity of the pathogen in a test tube and the sensitivity of the pathogen in the body may differ. This difference lies in the number of microorganisms in the body as a whole.
Unfortunately, there is no way to test directly from the organ.
Therefore, despite the fairly high accuracy of the analysis, it is necessary to remember that the identified sensitivity to the drug does not always coincide with the actual sensitivity of the patient’s body. Based on this, the doctor must monitor the use of the medicine so that the treatment is not wasted.
Urine-based test

As stated earlier, the analysis must be performed on sterile isolates of organisms. These primarily include urine.
Urine-based tests are indicated for patients with diseases in the urinary system.
Symptoms of such diseases include:
- pain when urinating;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- disturbances in the process of urination;
- changes in the results of urine tests;
- reaction to the use of antibiotics in the organs responsible for urination.
In order to conduct such an analysis, you will need a morning urine sample. It must be collected in a special sterile container. You can either buy this container or use any suitable household container, for example, a simple small jar. However, it must be sterilized before use.
When collecting, you do not need to use the first drops of urine and the last. This is how the urine that is most concentrated with microorganisms, if any, will be analyzed.
You should warn your doctor if you took antibiotics a few days before giving the sample. They may cause a false result.
The analysis will take up to ten days. The duration of the study depends on the microorganisms. During these ten days, the urine will be subjected to a series of tests, as a result of which the doctor will get an idea of the causative agent of the disease, its sensitivity and the antibiotic with which the most effective treatment will be carried out. effective treatment.
Blood based test

Like a urine test, an antibiotic sensitivity test, its decoding based on blood helps to understand whether the patient has the causative agents of a particular disease.
Blood is also a sterile body secretion and is often used in tests.
It should be taken before the patient starts taking antibiotics. If the collection was carried out after, the results may be false.
The collection is made from a vein. The amount ranges from five to ten milliliters.
After the blood has been drawn, it is placed in a special bottle in which a nutrient medium for bacteria has been prepared. Antibiotic sensitivity testing is performed. The analysis is deciphered based on the results after the process is completed.
The results of the analysis are revealed in sixteen or eighteen hours. The time varies depending on the type of pathogen. It is ultimately determined by the moment its growth becomes apparent.
This is how the type of pathogen is determined, after which the stability test begins.
Blood test results may be as follows:
- there are no pathogens in the blood;
- one type of pathogen was found;
- several types of pathogens.
The analysis and its interpretation, in which the sensitivity to antibiotics is indicated, are transferred to the doctor, and based on them, he determines the type of treatment, the drug, and its dosage.
An antibiotic sensitivity test is mandatory if the doctor suspects that the patient’s disease is bacterial in nature. This is due to the fact that doctors are trying to control the prescription of these drugs so as not to stimulate mutations and cause resistance in microorganisms.
Definition
Antibiotic sensitivity testing is a laboratory method for identifying a drug that will have greatest action on the pathogenic flora in this particular case of disease.
On at the moment Antibacterial therapy is used quite widely where it is needed, as well as in cases where it is not at all necessary, for reinsurance against possible complications. For example, after caesarean section, laparoscopic operations, removal of stones from the kidneys or ureters, etc.
The pharmaceutical industry can offer a wide range of drugs, both in terms of price and effectiveness. In order not to “point your finger at the sky” and prescribe an effective antibiotic, you need to conduct sensitivity cultures.
Indications
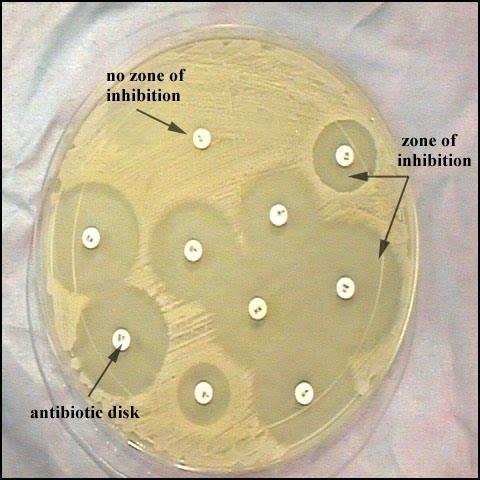
Before the doctor selects therapy, the patient must undergo some tests. Antibiotic sensitivity testing is prescribed if it is necessary to determine the drug that will be most appropriate in a given case. Most often, this test is prescribed to treat sexually transmitted diseases, or STDs. For children, the need to determine the antibiotic is a prerequisite.
In addition, sensitivity testing is necessary to avoid bacterial resistance to treatment. If the patient has recently been treated with antibiotics, and now a repeat course is needed again, then a change in drug is required. This will allow the use of smaller doses of the drug and not cause mutations in the pathogen. In purulent surgical departments, antibiotics are changed every two to three months.
This analysis is also necessary if the patient has an allergic reaction to the main group of antibiotics.
Diffusion methods

A urine test for sensitivity to antibiotics, and not only that, can be done in several ways. The first one is the disk method. It is carried out as follows. Agar is poured into a Petri dish, and when it hardens, the material to be tested is applied with a special tool. Then paper disks soaked in antibiotics are laid out on the surface of the agar. Afterwards the cup is closed and placed in a thermostat. Gradually, the disc is immersed in gelatin, and the antibiotic diffuses into the surrounding space. A zone of “growth suppression” forms around the paper. The cups are kept in the thermostat for twelve hours, then they are removed and the diameter of the above zone is measured.
The second method is the E-test method. It is similar to the previous one, but instead of paper discs they use a strip, which is impregnated with an antibiotic to varying degrees along its length. After twelve hours of exposure in the thermostat, take out the Petri dish and look at where the growth suppression zone comes into contact with the strip of paper. This will be the lowest concentration of the drug needed to treat the disease.
The advantage of these tests is the speed and ease of their implementation.
Breeding methods
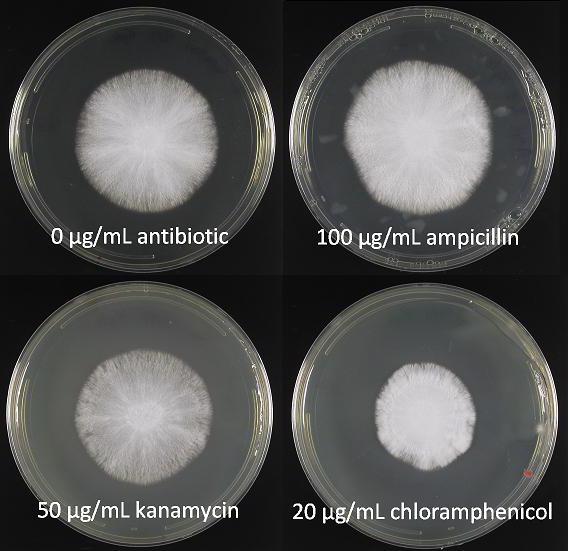

Analysis of flora and sensitivity to antibiotics can be carried out in another way. This method is based on a sequential decrease in the concentration of the antibiotic (from maximum to minimum) in order to determine in which of the tubes the inhibition of bacterial growth will cease.
First, drug solutions are prepared. Then they are added to a liquid medium with bacteria (broth or agar). All test tubes are placed in a thermostat at a temperature of 37 degrees overnight (that is, 12 hours), and the results are analyzed in the morning. If the contents of a test tube or Petri dish are cloudy, this indicates bacterial growth and, therefore, the ineffectiveness of the antibiotic at a given concentration. The first tube in which the growth of colonies of microorganisms is not visually determined will be considered a sufficient concentration for treatment.
This dilution of the drug is commonly called the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). It is measured in milligrams per liter or micrograms per milliliter.
Interpretation of results
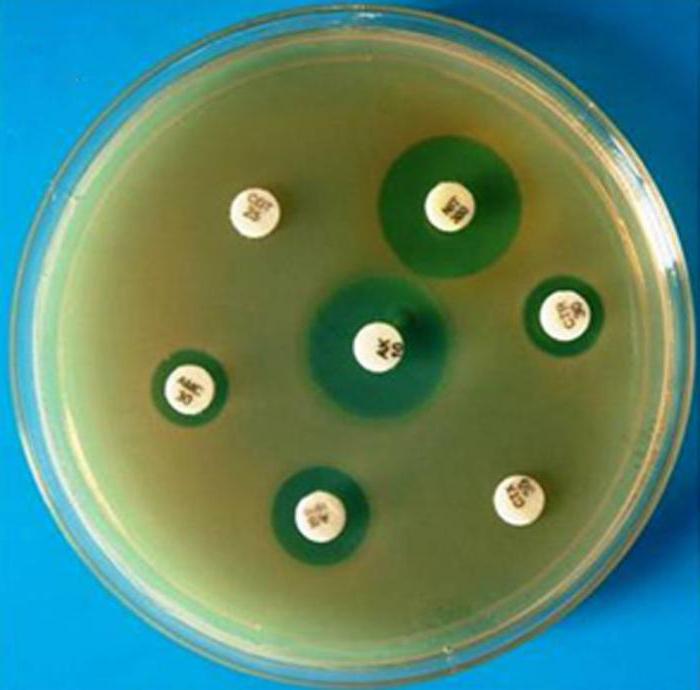
An antibiotic sensitivity test needs to be able to not only be done correctly, but also correctly deciphered. Based on the results obtained, all microorganisms are divided into sensitive, moderately resistant and resistant. In order to distinguish them from each other, conditional boundary concentrations of drugs are used.
These values are not constant and may change depending on the adaptability of microorganisms. Chemotherapists and microbiologists are entrusted with the development and revision of these criteria. One of the official structures of this kind is the US National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. The standards they developed are recognized worldwide for use in assessing the activity of antibiotics, including for randomized multicenter studies.
There are two approaches to assessing the results of antibiotic sensitivity testing: clinical and microbiological. Microbiological assessment is focused on the distribution of effective antibiotic concentrations, and clinical assessment is focused on the quality of antibacterial therapy.
Resistant and sensitive microorganisms
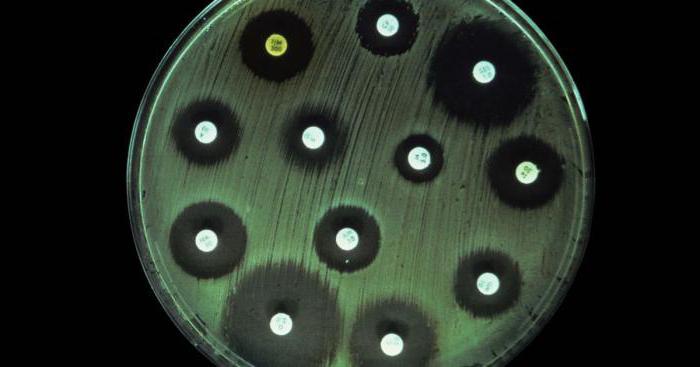
Analysis - determination of sensitivity to antibiotics - is prescribed to identify sensitive and resistant microorganisms.
Pathogens that can be treated with antibiotics in an average therapeutic concentration are called sensitive. If reliable information about the sensitivity category of a microorganism is not available, then data obtained in the laboratory are taken into account. They are combined with knowledge about the pharmacokinetics of the drug used, and after synthesizing this information, a conclusion is made about the susceptibility of bacteria to the drug.
Resistant, that is, resistant, microorganisms include those bacteria that continue to cause diseases even when using maximum concentrations of medicinal substances.
Intermediate resistance is established if the disease may have several outcomes during treatment. The patient's recovery is possible if high doses of antibiotics are used or if the drug is targeted at the site of infection.
Minimum bactericidal concentration
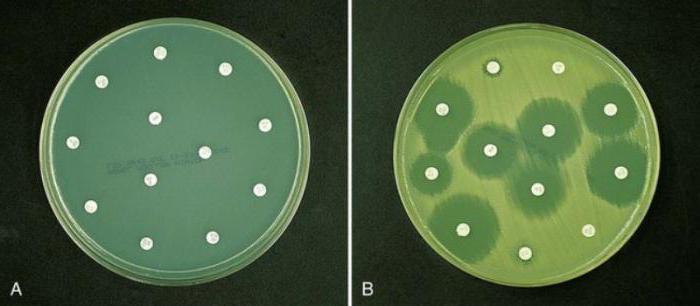
Analysis of microflora and sensitivity to antibiotics determines such an indicator as the minimum bactericidal concentration, or MBC. This is the lowest concentration of the drug, which in laboratory conditions causes the elimination of almost all microorganisms within twelve hours.
Doctors use knowledge of this indicator when prescribing therapy with bacteriostatic rather than bactericidal drugs. Or in cases where standard antibacterial therapy is ineffective. Most often, this analysis is ordered for patients with bacterial endocarditis, osteomyelitis, and also for opportunistic infections.
What could be a sample?
Antibiotic susceptibility testing can be performed using biological fluids:
Breast milk.
In addition, to determine local sensitivity, the cervical canal and upper respiratory tract are sampled.
Preparation for analysis
Antibiotic sensitivity testing does not require significant preparation from patients, but there are still some limitations.
- For the study, an average portion of morning urine is used, which is collected in a sterile container. Before this, the patient must perform toileting of the external genitalia and hands.
- Breast milk is collected before feeding the baby. The first portion is drained, and then a few milliliters from each breast are expressed into a sterile container.
- Before taking a nasopharyngeal swab, you should refrain from eating for five to six hours.
- In case of taking a smear from the genital tract, it is recommended to abstain from sexual intercourse for a couple of days.
To date, there are no clinical or laboratory methods that could predict the effect of antibacterial therapy with 100% certainty. But at the same time, determining the sensitivity of bacteria to drugs can be a guide for doctors in the selection and correction of treatment.
Show in full
Antibacterial therapy is the most widely used method of treating a wide range of diseases. This is due to the high efficiency and relative harmlessness of the method. However, it is not always possible to immediately select the necessary drugs.
Modern pharmaceuticals have provided medical specialists with a wide selection of antibacterial drugs. Often more than 3 different drugs are available to treat the same pathogen. An analysis of the antibiotic sensitivity testing.
Antibiotic sensitivity testing is used in the treatment of not only STDs, but also many others. infectious diseases. It is better to begin treatment of any disease for which antibacterial therapy is used by determining the sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms to antibiotics.
Why is antibiotic sensitivity testing necessary?
Carrying out such analyzes is necessary for several reasons:
- Determination of the most effective drug;
- Elimination of “addiction” of pathogenic microorganisms to therapy;
- Replacement of the drug due to ineffectiveness or allergic reactions;
- Reducing the treatment period.
Like any type of laboratory research, antibiotic sensitivity testing is absolutely safe and does not cause discomfort or pain. A sample of biomaterial is taken from the patient, and then studies are carried out in the laboratory.
Methods for determining sensitivity to antibiotics
Antibiotic discs
The dishes are inoculated with pathogenic microorganisms and discs soaked in antibiotics are placed on the surface of the dish. Based on the results of the destruction of microorganisms by an antibiotic, their sensitivity to each type of antibiotic is judged.
E-test
Strips soaked in antibiotics are placed in a nutrient medium. Effectiveness is judged by inhibiting the growth of pathogenic organisms.
Serial dilution method
The most accurate research method. Identical doses of pathogens are introduced into the nutrient medium with different concentrations of antibacterial agents. In this way, the minimum dose that effectively suppresses pathogenic microorganisms is determined.
What can serve as a model for research?
The sample of biomaterial is determined depending on the causative agent of the disease. Can be used:
- Saliva;
- Urine;
- Scraping;
- Breast milk;
- Prostate secretion;
- Cervical smear;
- Urethral swab;
- Swab from the back of the throat;
- Nasal swab;
- Sperm.
How to prepare for the analysis?
No special preparation is required. You just need to follow a few rules to get the most effective result.
- Saliva collects on an empty stomach;
- The first morning urine sample, collected in a sterile container, is suitable for analysis. Hygiene procedures before collecting urine are mandatory;
- When collecting samples from the cervical canal, urethra or prostate secretion, it is recommended to abstain from sexual activity for 1-2 days.
Antibiotic sensitivity testing will help determine antibacterial drugs, suitable for you. They will provide effective treatment, eliminate cases of relapse, and reduce the duration of treatment.

